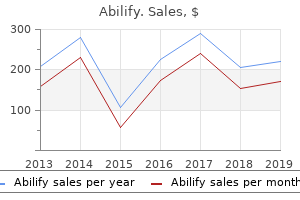
Abilify
"Purchase abilify online pills, depression symptoms ringing ears".
By: D. Potros, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Assistant Professor, Weill Cornell Medical College
Both parents must be studied after the confirmation to determine if one of them is a carrier and to aid with the interpretation of the finding(s) in case it is a polymorphic variant utter depression definition abilify 10mg otc. Consultation with a cytogeneticist or clinical genetics specialist is essential to interpret abnormal array results depression era order genuine abilify line. The most common microdeletion syndromes detected in newborns are described in Table 10 anxiety zone pancreatic cancer 10mg abilify fast delivery. They are caused by inherited or new mutations and often transmitted in a Mendelian fashion-like autosomal recessive depression visual symptoms purchase discount abilify on-line, autosomal dominant, and/or X-linked disorders. These include spinal muscular atrophy; congenital adrenal hyperplasia (most commonly due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency); congenital myotonic dystrophy (only when inherited from an affected mother); osteogenesis imperfecta due to type I collagen Table 10. Brain imaging studies and fundoscopic exam could reveal brain calcifications and/or chorioretinitis. The differential for nonimmune hydrops also includes several rare lysosomal storage disorders (see Chap. In most states, mandatory newborn screening is done initially between 24 and 48 hours of age, with a second screen done between 1 and 2 weeks of age. The March of Dimes and the American College of Medical Genetics recommend 29 conditions for testing. Most of these conditions can be managed by medications and/or special diets and treatments in many can be life saving. The anion gap should be measured in cases of acidosis; if the anion gap is increased, measure lactic acid in whole plasma from a free-flowing blood sample (ideally arterial), and measure organic acids in urine. Ultrasonography: brain imaging, to detect major malformation and intracranial hemorrhage; abdominal ultrasound exam, to detect major liver and kidney anomalies and presence and position of testicles/ovaries; and echocardiography, to detect heart defects. Muscle biopsy in children with severe hypotonia can be considered in conjunction with nerve biopsy to assess for disorders such as congenital muscular dystrophy, amyoplasia congenita, and hypomyelination syndromes. Sometimes, a muscle biopsy can be postponed until the infant is at least 6 months of age to gather better quality and more complete information. Autopsy studies in stillbirths or infants who died in the neonatal period may provide a diagnosis and help with counseling and recurrence risks. Good documentation should be obtained and radiographs should be considered in addition to pathologic exam. A sample of the placenta can also be submitted for genetic studies such as karyotyping. Patients with birth defects require close follow-up evaluation after hospital discharge either to aid in the diagnosis or to educate the family. Since approximately 50% of patients born with multiple congenital anomalies have no known diagnosis, the follow-up may reveal new findings that will contribute to the final diagnosis. This will help predict the natural history and allow a proper assessment of the recurrence risk. Infants suspected to be at risk for developmental delay should be referred for therapy services or early childhood intervention programs. Up-to-date online catalogue of Mendelian genetic disorders and traits with a useful search engine for the identification of syndromes. Triplets and higher order pregnancies (quadruplets, quintuplets, sextuplets, septuplets, etc. A major portion of the placenta and the fetal membranes originate from the zygote. The placenta consists of two parts: (i) a larger fetal part derived from the villous chorion and (ii) a smaller maternal part derived from the deciduas basalis. The chorion begins to form at day 3 after fertilization, and the amnion begins to form between days 6 and 8. This rate is influenced by several factors such as ethnicity (1 in 500 Asians, 1 in 125 in whites, and as high as 1 in 20 in African populations) and maternal age. The birth rate of triplet and higher order multiples peaked in 1998 at 194 per 100,000 live births. The rates for other higher order multiples (quadruplets and higher) 124 General Newborn Condition 125 declined by 21% in 2006 compared to peak rates in 1998 (194 per 100,000 live births). A dichorionic diamniotic placenta results when early splitting occurs at day 0 to 3 before chorion formation (which usually occurs about day 3) and before implantation. A monochorionic diamniotic placenta results when splitting occurs about day 4 to 7, at which time the blastocyst cavity has developed and the chorion has formed.
Diseases
- Malignant germ cell tumor
- Lowry Wood syndrome
- Nystagmus
- Koilonychia
- Oculocutaneous albinism, tyrosinase negative
- Mehta Lewis Patton syndrome
Granulocyte transfusions can only Hematologic Disorders 535 be used as a temporary therapy until the patient starts producing neutrophils or until another curative therapy can be instituted (see Chap mood disorder symptoms order 20mg abilify. Granulocyte collections need to be specially scheduled depression symptoms ptsd purchase cheap abilify online, and the granulocytes should be transfused as soon as possible after collection and no later than 24 hours after the collection depression easy definition order genuine abilify on-line. Whole blood may be useful for neonates immediately following disconnection from a cardiopulmonary bypass circuit for cardiac surgery bipolar depression checklist discount abilify express. All of the adverse effects of individual blood components can occur with whole blood. When used just after cardiopulmonary bypass, the blood should be no more than 2 to 3 days old. When used in other situations, the whole blood should be no more than 5 to 7 days old. Platelets in whole blood will be cleared rapidly following transfusion and reconstituted whole blood lacks significant quantities of platelets. Most products contain over 90% immunoglobulin G (IgG), with small amounts of immunoglobulin M (IgM) and immunoglobulin A (IgA). High titer disease-specific immunoglobulins are available for several infectious agents, including varicella zoster virus and respiratory syncytial virus. These immunoglobulins may be useful for infants at high risk for these infections (see Chap. If the mother and baby are healthy, the cord blood can be collected without any impact on the neonate. An entire cord blood is used for younger children and two cord bloods may be used for adult transplants. Cord bloods are usually infused into central veins as part of a hematopoietic cell transplant protocol. Randomized trial of liberal versus restrictive guidelines for red blood cell transfusion in preterm infants. Is white blood cell reduction equivalent to antibody screening in preventing transmission of cytomegalovirus by transfusion Neurodevelopmental outcome of extremely low birth weight infants randomly assigned to restrictive or liberal hemoglobin thresholds for blood transfusion. Neufeld the hemostatic mechanism in the neonate differs from that in the older child. In neonates, there is decreased activity of several clotting factors, diminished platelet function, and suboptimal defense against clot formation. The administration of total parenteral alimentation or antibiotics or the lack of administration of vitamin K to premature infants. Term infants may develop vitamin K deficiency by day 2 or 3 if they are not supplemented with vitamin K parenterally because of negligible stores and inadequate intake. Phenytoin (Dilantin), phenobarbital, and salicylates interfere with the vitamin K effect on synthesis of clotting factors. Any significant liver disease may interfere with the production of clotting factors by the liver. X-linked recessive (expressed predominantly in males; affected females should raise concern for Turner syndrome, partial X deletions, or nonrandom X-chromosome inactivation). Inherited marrow failure syndromes, including Fanconi anemia and congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia. Inherited thrombocytopenia syndromes, including gray platelet syndrome and the macrothrombocytopenias, such as May-Hegglin syndrome (6). First, this condition leads to platelet activation and risk of thrombosis more than bleeding. Finally, in neonates, the antibody may be maternal, as with other antibodies passed across the placenta. Other potential causes of bleeding are vascular in etiology and may include central nervous system hemorrhage, pulmonary hemorrhage, arterio-venous malformations, and hemangiomas. Subdural hematoma, cephalhematoma, or subgaleal hemorrhage (the latter may be associated with vacuum extraction). The history includes (i) family history of excessive bleeding or clotting, (ii) maternal medications (e.
Discount abilify 10 mg overnight delivery. STRUGGLING WITH POSTPARTUM ANXIETY..
Growth parameters must also be monitored so that continued growth is not compromised mood disorder va compensation order abilify online now. However depression definition army buy abilify 10 mg on-line, there is a paucity of data regarding what to feed the preterm infant after discharge depression symptoms anxiety purchase generic abilify pills. The use of human milk and efforts to transition to full breastfeeding in former preterm infants who continue to require enhanced caloric density feedings anxiety 30000 buy 15mg abilify with mastercard, poses a unique challenge. Individualized care plans are indicated in order to support the transition to full breastfeeding while continuing to allow for optimal rates of growth. Usually, this is accomplished by a combination of a specified number of nursing sessions per day, supplemented by feedings of calorically enhanced breast milk or nursing on demand supplemented by several feeds per day of nutrient-enriched postdischarge formula. In some of the trials, infants on standard formula increased their volume of intake, therefore, mostly compensating for any additional nutrients from the postdischarge formulas. However, the length of time after discharge these formulas should be continued remains unclear. Term formulas may also be utilized; however, careful monitoring of growth after discharge should continue. Iron supplementation guidelines for preterm infants are recommended as previously described. Enteral nutrient supply for preterm infants: commentary from the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. Nutritional Needs of the Premature Infant: Scientific Basis and Practical Guidelines. Birth to 24 months: boys head circumference-for-age and weight-for-length percentiles. Birth to 24 months: Girls head circumference-for-age and weight-for-length percentiles. Breastfeeding enhances maternal involvement, interaction, and bonding; provides species-specific nutrients to support normal infant growth; provides nonnutrient growth factors, immune factors, hormones, and other bioactive components that can act as biological signals; and can decrease the incidence and severity of infectious diseases, enhance neurodevelopment, decrease the incidence of childhood obesity and some chronic illnesses, and decrease the incidence and severity of atopic disease. When direct breastfeeding is not possible, expressed breast milk should be provided C. Complementary foods should be introduced around 6 months with continued breastfeeding up to and beyond the first year G. Common breast conditions experienced during early breastfeeding and basic management strategies. At 3 to 5 days postdelivery, the mother should experience some breast fullness, and notice some dripping of milk from opposite breast during breastfeeding; demonstrate ability to latch infant to breast; understand infant signs of hunger and satiety; understand expectations and treatment of minor breast/nipple conditions. If infant growth is inadequate, after ruling out any underlying health conditions in the infant, breastfeeding assessment should include adequacy of infant attachment to the breast; presence or absence of signs of normal lactogenesis. The ability of infant to transfer milk at breast can be measured by weighing the infant before and after feeding using the following guidelines. Weighing the diapered infant before and immediately after the feeding (without changing the diaper) ii. If milk transfer is inadequate, supplementation (preferably with expressed breast milk) may be indicated. Instructing the mother to express her milk with a mechanical breast pump following feeding will allow additional breast stimulation to increase milk production. A common description of this soreness includes an intense onset at the initial latch-on with a rapid subsiding of discomfort as milk flow increases. Nipple tenderness should diminish during the first few weeks until no discomfort is experienced during breastfeeding.
Ground Lily (Beth Root). Abilify.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Beth Root?
- How does Beth Root work?
- Heavy menstruation and pain, reducing swelling (astringent), breaking up chest congestion, varicose veins, ulcers, blood clots, and bleeding hemorrhoids.
- Dosing considerations for Beth Root.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96416