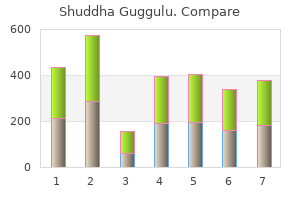
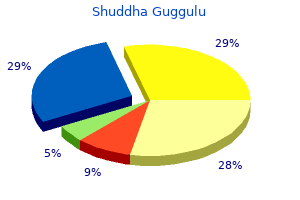
Shuddha Guggulu
"60 caps shuddha guggulu overnight delivery, weight loss detox tea".
By: Y. Ramirez, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Central Michigan University College of Medicine
The temperature information represented in that electrical signal is passed to the next neuron by a chemical signal that diffuses across the small gap of the synapse and initiates a new electrical signal in the target cell weight loss help buy cheap shuddha guggulu 60 caps. That signal travels through the sensory pathway to the brain weight loss detox generic shuddha guggulu 60 caps fast delivery, passing through the thalamus weight loss juicing plan purchase shuddha guggulu 60caps, where conscious perception of the water temperature is made possible by the cerebral cortex weight loss blogs for women buy cheap shuddha guggulu 60caps online. Following integration of that information with other cognitive processes and sensory information, the brain sends a command back down to the spinal cord to initiate a motor response by controlling a skeletal muscle. The motor pathway is composed of two cells, the upper motor neuron and the lower motor neuron. The upper motor neuron has its cell body in the cerebral cortex and synapses on a cell in the gray matter of the spinal cord. The lower motor neuron is that cell in the gray matter of the spinal cord and its axon extends into the periphery where it synapses with a skeletal muscle in a neuromuscular junction. Whether those areas are close or very far apart, the signal must travel along an axon. Transmembrane ion channels regulate when ions can move in or out of the cell, so that a precise signal is generated. This signal is the action potential which has a very characteristic shape based on voltage changes across the membrane in a given time period. The membrane is normally at rest with established Na+ and K+ concentrations on either side. A stimulus will start the depolarization of the membrane, and voltage-gated channels will result in further depolarization followed by repolarization of the membrane. While an action potential is in progress, another cannot be generated under the same conditions. While the voltage-gated Na+ channel is inactivated, absolutely no action potentials can be generated. Once that channel has returned to its resting state, a new action potential is possible, but it must be started by a relatively stronger stimulus to overcome the K+ leaving the cell. The action potential travels down the axon as voltage-gated ion channels are opened by the spreading depolarization. In unmyelinated axons, this happens in a continuous fashion because there are voltage-gated channels throughout the membrane. In myelinated axons, propagation is described as saltatory because voltage-gated channels are only found at the nodes of Ranvier and the electrical events seem to "jump" from one node to the next. Saltatory conduction is faster than continuous conduction, meaning that myelinated axons propagate their signals faster. The diameter of the axon also makes a difference as ions diffusing within the cell have less resistance in a wider space. For a neuron to generate an action potential, it needs to receive input from another source, either another neuron or a sensory stimulus. That input will result in opening ion channels in the neuron, resulting in a graded potential based on the strength of the stimulus. Graded potentials can be depolarizing or hyperpolarizing and can summate to affect the probability of the neuron reaching threshold. If the sensory stimulus is received by the dendrites of a unipolar sensory neuron, such as the sensory neuron ending in the skin, the graded potential is called a generator potential because it can directly generate the action potential in the initial segment of the axon. If the sensory stimulus is received by a specialized sensory receptor cell, the graded potential is called a receptor potential. Synapses are the contacts between neurons, which can either be chemical or electrical in nature. At a chemical synapse, neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic element and diffuses across the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitter must be inactivated or removed from the synaptic cleft so that the stimulus is limited in time. The particular characteristics of a synapse vary based on the neurotransmitter system produced by that neuron.
Lack of cooperation during the diagnostic evaluation and in complying with the pre scribed treatment regimen weight loss pills kidney transplant buy 60caps shuddha guggulu with mastercard. Malingering differs from factitious disorder in that the motivation for the symptom production in malingering is an external incentive weight loss 30 pounds purchase generic shuddha guggulu online, whereas in factitious disorder external incentives are absent weight loss foods purchase shuddha guggulu 60caps otc. Malingering is differentiated from conversion disorder and somatic symptom-related mental disorders by the intentional production of symptoms and by the obvious external incentives associated with it weight loss pills uk shuddha guggulu 60 caps low price. For example, individuals with major neurocognitive or neurodevelopmental disorders may experience a restless urge to wander that places them at risk for falls and causes them to leave supervised settings with out needed accompaniment. This category excludes individuals whose intent is to escape an unwanted housing situation. Differ entiating borderline intellectual functioning and mild intellectual disability (intellectual developmental disorder) requires careful assessment of intellectual and adaptive functions and their discrepancies, particularly in the presence of co-occurring mental disorders that may affect patient compliance with standardized testing procedures. Proposed disorders for future study are provided, which include a new model for the diagnosis of personality disorders as an alternative to the estab lished diagnostic criteria; the proposed model incorporates impairments in per sonality functioning as well as pathological personality traits. Also included are new conditions that are the focus of active research, such as attenuated psy chosis syndrome and nonsuicidal self-injury. Assessrilbnt Measures A growing body of scientific evidence favors dimensional concepts in the diagnosis of mental disorders. The limitations of a categorical approach to diagnosis include the fail ure to find zones of rarity between diagnoses. For diagnoses for which all symptoms are needed for a diagnosis (a monothetic criteria set), different se verity levels of the constituent symptoms may be noted. If a threshold endorsement of multiple symptoms is needed, such as at least five of nine symptoms for major depressive disorder (a polythetic criteria set), both severity levels and different combinations of the criteria may identify more homogeneous diagnostic groups. It is expected that as our understanding of basic disease mechanisms based on pathophysiology, neurocircuitry, gene-environment interactions, and laboratory tests increases, approaches that integrate both objective and subjective patient data will be developed to supplement and enhance the accuracy of the diagnostic process. The general med ical review of systems is crucial to detecting subtle changes in different organ systems that can facilitate diagnosis and treatment. The cross-cutting measures have two levels: Level 1 questions are a brief survey of 13 symptom domains for adult patients and 12 domains for child and adolescent patients. Severity measures are disorder-specific, corresponding closely to the criteria that consti tute the disorder definition. They may be administered to individuals who have received a diagnosis or who have a clinically significant syndrome that falls short of meeting full criteria for a diagnosis. Some of the assessments are self-completed by the individual, while others require a clinician to complete. The scale is self-administered and was developed to be used in patients with any medical disorder. Clinician instructions, scoring information, and interpretation guidelines are included for each. These measures and additional dimensional assessments, including those for diagnostic severity, can be found online at The adult version of the measure consists of 23 questions that assess 13 psychiatric do mains, including depression, anger, mania, anxiety, somatic symptoms, suicidal ideation, psychosis, sleep problems, memory, repetitive thoughts and behaviors, dissociation, per sonality functioning, and substance use (Table 1). Each item inquires about how much (or how often) the individual has been bothered by the specific symptom during the past 2 weeks. The parent/guardian-rated version of the measure (for children ages 6-17) consists of 25 questions that assess 12 psychiatric domains, including depression, anger, irritability, mania, anxiety, somatic symptoms, inattention, suicidal ideation/attempt, psychosis, sleep disturbance, repetitive thoughts and behaviors, and substance use (Table 2). Each item asks the parent or guardian to rate how much (or how often) his or her child has been bothered by the specific psychiatric symptom during the past 2 weeks. On the adult self-rated version of the measure, each item is rated on a 5-point scale (O=none or not at all; l=slight or rare, less than a day or two; 2=mild or several days; 3=moderate or more than half the days; and 4=severe or nearly every day). As such, indicate the highest score within a domain in the "Highest domain score" column. Table 1 outlines threshold scores that may guide further inquiry for the remaining domains.
Purchase shuddha guggulu uk. எவ்ளோ ஒல்லியா இருந்தாலும் உடல் சூட்டை குறைத்து எடை கூட்டிடலாம் | weight gain tips|saudi tamil mom.
Unfortunately weight loss workout plan for women purchase shuddha guggulu without a prescription, in clinical practice weight loss pills 7767 order shuddha guggulu mastercard, the distinction between acute and chronic hyponatraemia is often unclear weight loss pill 90 purchase 60 caps shuddha guggulu with amex, particularly for patients presenting to the emergency room weight loss pills all natural discount shuddha guggulu 60caps without a prescription. If classifying hyponatraemia as acute or chronic is not possible, we have decided to consider hyponatraemia as being chronic, unless there are reasons to assume it is acute (Table 9). Chronic hyponatraemia is much more common than acute hyponatraemia and should be managed accordingly to avoid osmotic demyelination (85, 86). The distinction is based on selected observations in acute hyponatraemia; those who subsequently die more often experience what we define as severe symptoms than those who live (73, 74). Moderately severe symptoms caused by brain oedema are less frequently associated with death. Nevertheless, they may rapidly progress to more severe symptoms associated with an adverse outcome. Very limited and subclinical signs such as mild concentration deficits are seen even with mild hyponatraemia (13). A classification based on symptoms aims to reflect the degree of brain oedema and the extent of immediate danger. It allows matching treatment to the immediate risk, with more aggressive treatment for symptoms that are more severe. Nevertheless, a classification based only on symptom severity has several shortcomings. Secondly, patients with acute hyponatraemia can present without clear symptoms, but go on to develop moderately severe to severe symptoms within hours (73). Clinicians need to be wary that symptoms can be caused by conditions other than hyponatraemia, by other conditions in combination with hyponatraemia or by conditions that cause hyponatraemia. In general, one should be particularly careful when attributing moderately severe to severe symptoms to hyponatraemia when the biochemical degree of hyponatraemia is only mild (Table 5). Classification based on serum osmolality As this guideline aimed to cover the aspects of diagnosis and treatment specifically of hypotonic hyponatraemia, we needed to define what distinguishes hypotonic from non-hypotonic hyponatraemia. Because this distinction is a necessary first step in the diagnostic evaluation of any hyponatraemia, we have devoted a separate section to this topic (section 6. Classification based on volume status Patients with hyponatraemia may be hypovolaemic, euvolaemic or hypervolaemic (87). Many traditional diagnostic algorithms start with a clinical assessment of volume status (88). However, it is often not clear whether volume status in this context refers to the extracellular fluid volume, to the effective circulating volume or to the total body water. In addition, the sensitivity and specificity of clinical assessments of volume status are low, potentially leading to misclassification early in the diagnostic tree (89, 90). Note of caution We wanted the classification of hyponatraemia to be consistent, easy to use and helpful for both differential diagnosis and treatment. Hyponatraemia can be classified according to different factors, each with advantages and pitfalls depending on the clinical setting and situation. We have prioritised the criteria such that we would obtain a classification that would be clinically relevant and as widely applicable as possible. Nevertheless, the user should keep in mind that differential diagnosis of hyponatraemia is difficult and no classification can be 100% accurate in every situation. We emphasise that the different classifications of hyponatraemia are not mutually exclusive and that classification should always occur with the clinical condition and the possibility of combined causes of hyponatraemia in mind. Is it possible to identify symptoms or parameters that can reliably differentiate acute from chronic hyponatraemia Non-hypotonic hyponatraemia does not cause brain oedema and is managed differently from hypotonic hyponatraemia. As this guideline covers management of hypotonic hyponatraemia, confirmation of hypotonicity is a prerequisite. Effective osmoles Exogenous or endogenous solutes to which cell membranes are impermeable are restricted to the extracellular fluid compartment and are effective osmoles because they create osmotic pressure gradients across cell membranes leading to osmotic movement of water from the intracellular to the extracellular compartment (34, 36). Because dilutional hyponatraemia results from the water shift from the intracellular to the extracellular compartment, there is no risk of brain oedema. Depending on the serum concentration of effective osmoles, the resulting nonhypotonic hyponatraemia can be isotonic or hypertonic. Others include infusion of mannitol or perioperative absorption of irrigation fluids such as glycine (32, 33).
Pomalidomide is a derivative that has activity in subjects who are resistant to lenalidomide weight loss pills before and after order shuddha guggulu 60 caps online. Other options include melphalan and (intermittent oral) prednisolone (+/- thalidomide); further courses of bortezomib or its newer derivatives weight loss pills xenadrine review buy shuddha guggulu 60caps low price. Younger patients (those under 65) with myeloma may benefit from intensive therapy weight loss water recipe purchase 60caps shuddha guggulu with amex, including autologous transplant of peripheral blood stem cells weight loss pills like oxyelite pro purchase shuddha guggulu 60caps otc. The nucleated red cells show an open nuclear chromatin pattern (most clearly seen on the high-power view of erythroblasts, Figure 2d). A radioactive carbon breath test would be a helpful further investigation, as it would exclude the presence of an intestinal stagnant loop with bacterial overgrowth. Six weeks later, she developed a febrile illness with facial swelling and orbital oedema (Figure 3b). She also became short of breath and hypotensive, and had a single episode of haemoptysis. The marked facial cellulitis would be compatible with a Gram-positive skin infection but an x-ray of her sinuses should also be carried out. Cavitation should be carefully looked for, and, if present, would support a diagnosis of staphylococcal pneumonia. Every attempt must be made to make a microbiological diagnosis (blood cultures, culture of aspirate from skin, sputum culture, possibly bronchoalveolar lavage). She should receive broad-spectrum antibiotic and anti-fungal therapy, and this should include systemic liposomal amphotericin or some other lipid formulation of amphotericin B. Oral itraconazole is used as prophylaxis and intravenous itraconazole is active in the treatment of aspergillosis. Caspofungin is a newer anti-fungal agent active in both candidiasis and aspergillosis. Voriconozole has a broader spectrum of activity; posaconazole has recently become available for prophylaxis and treatment for invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised individuals. This patient may have hypercalcaemia (which can lead to renal failure) and the alkaline phosphatase (bone isoenzyme) may be raised. Immunocytochemistry and flow cytometry may be used to confirm the origin of the infiltrating cells, for example, epithelial cells are usually positive for cytokeratin. Other tumours that frequently affect the marrow include tumours of the bronchus (Figure 4d), prostate, renal and thyroid, and neuroblastoma in childhood (Figure 4e). The coagulation tests are normal, effectively excluding disseminated intravascular coagulation, and the creatinine is normal, excluding haemolytic uraemic syndrome. If mucosal bleeding occurs, treatment should be considered and it is reasonable to exclude other causes of thrombocytopenia (drugs, infection including rubella, infectious mononucleosis, hepatitis C, bacterial infections). A bone marrow aspirate (Figure 5d) confirms the presence of megakaryocytes (large, multinuclear cells), thus suggesting platelet destruction. Platelet antibody testing is of much less value than the corresponding tests for red cells. Romiplostin has to be given by parenteral injection whereas eltrombopag can be given orally. Splenectomy is best avoided in children under five and should, in any event, be preceded by vaccination against pneumococcus and Haemophilus influenzae B, and followed by long-term oral penicillin V as prophylactic therapy against infection. Her menstrual period has been going on for 10 days, and she has also noticed blood loss when brushing her teeth. It can also be used as first-line treatment in patients who are unsuitable for intensive chemotherapy; however, it is cardiotoxic and must be carefully monitored. The presence of more than one ring form per red cell strongly suggests Plasmodium falciparum.