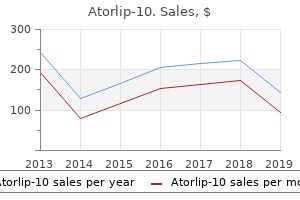
Atorlip-10
"Buy atorlip-10 10 mg fast delivery, non hdl cholesterol definition".
By: E. Cruz, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Baylor College of Medicine
Patients most commonly have ambiguous genitalia cholesterol test high order atorlip-10 10 mg visa, but near-normal female and male genitalia may be present cholesterol levels male atorlip-10 10 mg sale. A unicornuate or bicornuate uterus is usually present cholesterol levels gpnotebook buy cheap atorlip-10 10mg line, and the differentiation of the genital ducts is determined by the ipsilateral gonad cholesterol emboli syndrome cheap atorlip-10 10mg fast delivery, with the ovary usually located on the left side (5). The most common gonad found is the ovotestes (50%), followed by ovary (30%) and testes (20%). Combinations are ovotestes/ovary (34%), bilateral ovotestes (27%), ovary and testes (27%) and ovotestes/testes (12%). A well masculinized patient may rarely present after puberty with gynecomastia, cyclical hematuria, or scrotal pain secondary to ruptured ovarian follicles. In most patients, the external genitalia are masculinized to some extent, and two thirds of true hermaphrodites are raised as males. Of those raised as males, 80 percent have hypospadias and over 50 percent have labioscrotal fusion. The ovary is found in a normal location, but the testes or ovotestes may be at any point along the path of testicular descent (5). In addition to imaging studies, a gonadal biopsy is necessary to prove the existence of both ovarian and testicular tissue. Dysgenetic gonads (histologically disordered gonads) are noted primarily in mixed gonadal dysgenesis, pure gonadal dysgenesis, and gonadal dysgenesis (Turner Syndrome). A testis is usually found intraabdominally opposite a streak gonad (resembling ovarian stroma histologically). A unicornuate (only one side of the uterus is present) uterus, fallopian tubes and vagina are present. The genitalia are ambiguous with severe hypospadias, a urogenital sinus, and labioscrotal fusion, with an undescended testicle. One third exhibit Turner stigmata (short stature, shield like chest, webbed neck, multiple pigmented nevi, and cubitus valgus) as well as cardiovascular and renal anomalies (5,6). The incidence of gonadal tumors is 25 percent in patients with mixed gonadal dysgenesis and may arise in the streak gonad or the undescended testes. Early bilateral gonadectomy with female rearing is appropriate in phenotypic females. In phenotypic males with a scrotal testes, male rearing is appropriate, but the streak gonads must be removed. Pure gonadal dysgenesis is an abnormal differentiation of the gonads without a chromosomal abnormality. They usually present as adolescent females who fail to mature and reach menarche (5). These patients with the Y chromosome are at high risk for the development of gonadal tumors, so prophylactic gonadectomy is indicated (6,8). As neonates do not have ambiguous genitalia, the syndrome is usually diagnosed from investigations for other neonatal anomalies, which include: intrauterine growth retardation, head and facial anomalies, lymphatic anomalies, cardiovascular or urinary tract malformations or skeletal anomalies) (8). All should be raised as females, with gonadectomy indicated only in those with virilization or with clear evidence of a Y cell-line (6,8). In the delivery room, no attempt should be made to suggest a diagnosis or assign a gender. The parents should be told that development is incomplete and further tests will reveal the appropriate gender. Examination of the child in the presence of the parents to demonstrate the precise abnormalities of genital development is helpful, noting that the genitalia of both sexes develop from the same primordial structures, that both incomplete development or overdevelopment of the external genitalia can occur, and that the abnormal appearance can be corrected and the child raised as a boy or girl, as appropriate (3). A family should never be told that their child is male, but will be made female, or vice versa. Parents should be encouraged not to name the child or register the birth, if possible, until the sex of rearing is established. The parents need to be included in the discussions regarding sex of rearing decisions. Transfer of the child to a tertiary care facility is usually necessary for optimal assessment and treatment. A multidisciplinary medical team, with representation from neonatology, endocrinology, urology, psychiatry and genetics services is useful.
C Interfering factors Drugs that may cause false-positive results include antiarrhythmics foods that decrease cholesterol discount atorlip-10 10mg mastercard, antituberculins lipitor cholesterol medication side effects cheap atorlip-10 online amex, cephalosporins cholesterol lowering foods crossword purchase atorlip-10 toronto, chlorpromazine cholesterol ratio levels order 10mg atorlip-10 visa, insulin, levodopa, methyldopa, penicillin, phenytoin, quinidine, sulfonamides, and tetracyclines. Remember that if this antibody screening test is positive, antibody identification is then done. Cortisol tends to increase glucose by stimulating gluconeogenesis from glucose stores. It also inhibits the effect of insulin and thereby inhibits glucose transport into the cells. The best method of evaluating adrenal activity is by directly measuring plasma cortisol levels. Normally cortisol levels rise and fall during the day; this is called the diurnal variation. Cortisol levels are highest around 6 am to 8 am and gradually fall during the day, reaching their lowest point around midnight. Sometimes the earliest sign of adrenal hyperfunction is only the loss of this C Test explanation and related physiology 302 cortisol, blood, urine, saliva diurnal variation, even though the cortisol levels are not yet elevated. For example, individuals with Cushing syndrome often have upper normal plasma cortisol levels in the morning and do not exhibit a decline as the day proceeds. High levels of cortisol indicate Cushing syndrome, and low levels of plasma cortisol are suggestive of Addison disease. Normal values may be transposed in individuals who have worked during the night and slept during the day for long periods of time. The measurement of late-night salivary cortisol is another effective test for Cushing syndrome. It seems to be more convenient and superior to plasma and urine for detecting cortisol in patients with mild Cushing syndrome. Salivary cortisol assay cannot be used to diagnose hypocortisolism or Addison disease because laboratory methods are not sensitive enough at low levels. If late-night salivary cortisol levels are elevated, the results should be confirmed with a repeat salivary cortisol measurement, a midnight blood sampling for cortisol, or a 24-hour urinary collection of free cortisol. Stress stimulates the pituitary-cortical mechanism and thereby stimulates cortisol production. Drugs that may cause increased levels include amphetamines, cortisone, estrogen, oral contraceptives, and spironolactone (Aldactone). Drugs that may cause decreased levels include androgens, aminoglutethimide, betamethasone and other exogenous steroid medications, danazol, lithium, levodopa, metyrapone, and phenytoin (Dilantin). Because C-peptide has a longer half-life than insulin, more C-peptide exists in the peripheral circulation. The capacity of the pancreatic beta cells to secrete insulin can be evaluated by directly measuring either insulin or C-peptide. Direct insulin measurement in these patients tends to be high because the insulin measured is the self-administered exogenous insulin. But C-peptide levels in that same specimen will be low because exogenously administered insulin suppresses endogenous insulin (and C-peptide) production. This is done to see if the diabetic patient is in remission and may not need exogenous insulin. A person whose pancreas does not make any insulin (type I diabetes) has low levels of insulin and C-peptide. Furthermore, C-peptide is used in evaluating patients who are suspected of having an insulinoma. A rise in C-peptide levels indicates a recurrence or progression of the insulinoma. Likewise, some clinicians use C-peptide testing as an indicator of the adequacy of therapeutic surgical pancreatectomy C-peptide 305 in patients with pancreatic tumors.
If repeat tests show persistent abnormalities or if compliance is an issue cholesterol in eggs good buy atorlip-10 australia, colposcopy and directed biopsy may be indicated (2) cholesterol levels meaning purchase atorlip-10 without prescription. In general cholesterol levels and what they mean discount atorlip-10 express, there are patient-applied and provider-applied modalities of treatment heart healthy cholesterol lowering foods 10 mg atorlip-10 amex. Patients may apply podofilox solution or gel or imiquimod cream to visible lesions. Surgical removal is indicated if topical therapy fails, for extensive lesions, or for a young patient who requires general anesthesia (4). No clear evidence exists to determine whether treatment of genital warts will reduce transmission (2). All adolescent women with anogenital warts should have a Pap smear, with follow-up recommended every 6 months (4). Types D through K are responsible for the majority of genital infections, including mucopurulent cervicitis, urethritis, proctitis, epididymitis, salpingitis, endometritis, and perihepatitis. Ocular trachoma (a chronic follicular keratoconjunctivitis which is a common cause of acquired blindness in other countries), is caused by types A-C (4). Up to 85% of women and 40% of men who are infected with chlamydia are asymptomatic (3). Chlamydia urethritis should be suspected in sexually active females with prolonged dysuria (greater than 7-10 days) unresponsive to traditional treatment for bacterial cystitis (J). In males, chlamydial infection can also cause non-gonococcal urethritis, acute epididymitis, or proctitis. Although cervical culture for chlamydia is costly and technically difficult (it requires cell media culture because it is an obligate intracellular organism similar to a virus), it remains the gold standard and the procedure against which new diagnostic methods are measured (4). Tests for detecting chlamydial antigen have a sensitivity of approximately 60-80% (7). Preventive Services Task Force strongly recommends that "all sexually active women 25 years and younger and other asymptomatic women at increased risk of infection" be routinely screened for chlamydial infection. Urine-based home testing for chlamydia is expected to increase availability of low-cost screening (7). Azithromycin is an alternative regimen for pregnant women or patients for whom compliance is an issue (2). Patients should be encouraged to refer their sexual partners for diagnosis and treatment to prevent reinfection (2). A test of cure should be performed approximately 6 weeks after completion of treatment (7). This is suggested by the triad of: 1) abdominal pain, 2) uterine/adnexal tenderness on bimanual exam, and 3) cervical motion tenderness. Empiric treatment should be initiated if no other cause for these symptoms can be identified. If necessary, the diagnosis can be confirmed by: a) endometrial biopsy showing endometritis; b) transvaginal sonography demonstrating fluid-filled fallopian tubes, free pelvic fluid, or a tubo-ovarian complex (abscess); or c) laparoscopy. Differential diagnosis may include acute appendicitis, ectopic pregnancy, ruptured corpus luteum cyst with hemorrhage, diverticulitis, septic abortion, adnexal torsion, leiomyoma degeneration, endometriosis, or ulcerative colitis. A combination of clindamycin, gentamicin, and doxycycline is an alternative regimen (2). Gonorrhea Neisseria gonorrhoeae, a gram-negative intracellular diplococcus, is a commonly found co-infection with chlamydia. Hematogenous dissemination to joints, skin, meninges, and endocardium may occur (4). Overall, the rates of diagnosis are declining, but still remain high among adolescents aged 15 to19 of all racial and ethnic groups (2). Males infected with gonorrhea often present with symptomatic urethritis within 2 to 5 days of exposure, with urethral discharge or dysuria (7). Other manifestations in the male include epididymitis, lymphangitis, or prostatitis. In young women, the endocervical canal and urethra are the primary sites of infection.
It is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen cholesterol in foods chart discount atorlip-10 online amex, beneath the liver edge (1) cholesterol results chart buy discount atorlip-10. It is best palpated from the left side while the infant is feeding since the abdominal muscles are relaxed cholesterol test exercise before buy genuine atorlip-10. The diagnostic test of choice is the ultrasound cholesterol score of 206 order atorlip-10 10mg otc, which has approximately 90% sensitivity (1). Criteria for diagnosis include an elongated pyloric channel (longer than 16 mm), an enlarged pyloric diameter (greater than 14 mm), and a thickened muscle wall (greater than 3. Levels of glucuronyltransferase can be decreased in a small percentage of infants, as the liver is deprived of substrate from poor caloric intake, leading to an indirect hyperbilirubinemia (2). Vomiting in infants under 1 month of age is more likely due to a serious cause (often one requiring surgical intervention). Vomiting in older infants is more often secondary to gastroenteritis, but serious etiologies occur which may be difficult to diagnose. However, due to the improvements in surgical technique and associated lower mortality and morbidity rates, as well as the rapidity of the resolution of symptoms, pyloromyotomy is now the treatment of choice. Post-operative vomiting may occur secondary to edema of the pylorus at the incision site. In cases of incomplete pyloromyotomy, endoscopic balloon dilation has been successful. Medical Treatment of Idiopathic Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis: Should We Marinate or Slice the "Olive" A 3 to 4 week old male infant who presents with progressively severe, non-bilious vomiting, which may be projectile. The vomiting occurs immediately after feeding, after which the infant is still hungry and wants to feed again. A palpable "olive" is pathognomonic but is very difficult to determine with certainty. The "classic" laboratory finding is a hypochloremic, hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis. However, due to more expedient diagnosis, this metabolic abnormality is seen in less than 10% of patients. The initial step in management involves fluid resuscitation and correction of any metabolic abnormalities. Pattern "c" is a picture of vomiting resulting in dehydration and lactic acidosis. Roytman this is a newborn infant male born to a 25 year old G1P1A0 mother at 36 weeks gestation via vaginal delivery. The baby looked normal at birth, however, at 1 day of age (day 2 of life), the infant begins to vomit bilious material and appears jaundiced. An echocardiogram and radiographic studies of the spine are performed to evaluate for other congenital abnormalities. No other abnormalities are found and the patient is referred to surgery for surgical evaluation and treatment. Atresia, by definition, is the absence of an opening of a hollow visceral organ, resulting in a complete obstruction (1). There are several types of atresias: esophageal atresia with and without tracheoesophageal fistula, duodenal atresia, jejunal atresia and ileal atresia. Approximately one third of infants with esophageal atresia are born prematurely (2). In rare instances, infants have a tracheoesophageal fistula without an esophageal atresia. Esophageal atresias should be suspected if any one of the following is present: maternal polyhydramnios (from inability of the fetus to swallow and absorb amniotic fluid); excessive oral secretions in the newborn; cyanosis, choking, regurgitation or coughing occurring with the first feeding. If suspected, the diagnosis of an esophageal atresia can be confirmed by inability to pass the nasogastric tube into the stomach and by a chest radiograph, which shows the coiling of the tube in the proximal esophageal pouch. Injection of 1mL of contrast into the obstructed esophageal segment can also assist with the diagnosis (3). Postoperatively, an esophagogram should be performed before feeding is resumed to determine the integrity of the anastomosis of the two ends of the esophagus. Other complications of the disease are failure to thrive, slow feeding, esophageal stenosis, recurrent aspiration pneumonia, reactive airway disease, severe gastroesophageal reflux, coughing and choking (2).
Cheap atorlip-10 online visa. How to Reduce Cholesterol in Malayalam.