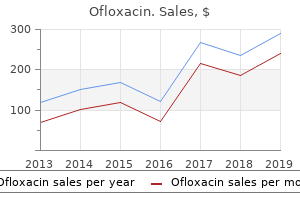
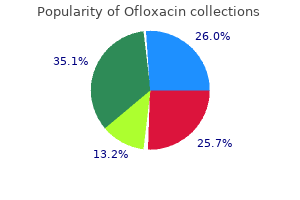
Ofloxacin
"Buy ofloxacin 200 mg overnight delivery, antibiotics used for diverticulitis".
By: J. Ismael, M.A., M.D.
Professor, Marian University College of Osteopathic Medicine
Prevention and treatment of uterine haemorrhage Bleeding due to incomplete abortion can be controlled with ergometrine and oxytocin (Syntometrine) given intramuscularly antibiotics for esbl uti generic ofloxacin 200mg with visa. For the routine management of the third stage of labour ergometrine 500 micrograms with oxytocin 5 units (Syntometrine 1 mL) is given by intramuscular injection on delivery of the anterior shoulder or antibiotics for uti how long does it take to work cheap 200mg ofloxacin otc, at the latest antibiotic 93 3160 best buy for ofloxacin, immediately after the baby is delivered antimicrobial bedding order ofloxacin 200mg with visa. Carboprost is an alternative for haemorrhage unresponsive to ergometrine and oxytocin. Induction of abortion Gemeprost, administered vaginally as pessaries, is the preferred prostaglandin for the medical induction of late therapeutic abortion. Gemeprost ripens and softens the cervix before surgical abortion, particularly in primigravida. Their use is complicated by the expected cardiovascular effects, including tachycardia, hypotension. Less easy to explain, but more devastating on occasion to the patient, is severe left ventricular failure. The combination of fluid overload (due to the vehicle) and increased oxygen demand by the heart are possible factors; the risk is higher in multiple pregnancy, pre-existing cardiac disease or maternal infection. It is important to administer the b2 agonist with minimum fluid volume using a syringe pump with 5% dextrose (not saline) as diluent, and to monitor the patient closely for signs of fluid overload. Induction and augmentation of labour Oxytocin is administered by slow intravenous infusion as below, usually in conjunction with amniotomy, and dinoprostone by vaginal tablets, pessaries and vaginal gels. Dinoprostone and oxytocin are equally effective for the induction of labour in women with ruptured membranes, regardless of parity or cervical favourability. Intravaginal dinoprostone preparations are preferable to intracervical preparations. New drugs for hyponatraemia: evidence is lacking that they are better than cheaper standard treatment. Effects of raloxifene on cardiovascular events and breast cancer in postmenopausal women. This idea has prompted a number of clinical trials examining the potential benefit of vitamin supplementation in the prevention of cancer, cardiovascular disease and other common diseases. With the exception of vitamin D, there is little robust evidence to support this claim and, for most consumers, over-the-counter vitamin preparations are probably of little more than placebo value. Fortunately, most vitamins are comparatively non-toxic; however, prolonged administration of vitamin A and vitamin D can have serious ill-effects. In addition to maintaining adequate nutritional levels, a number of vitamins can be used at pharmacological doses for therapy. The nutritional aspects, physiological function, sources, daily requirements and deficiency syndromes (primary and secondary) are to be found in any textbook of medicine. Vitamins1 are substances that are essential for normal metabolism but are supplied chiefly in the diet. Humans cannot synthesise vitamins in the body except some vitamin D in the skin and nicotinamide from tryptophan. This may be primary (inadequate diet) or secondary, due to failure of absorption (intestinal abnormality or chronic diarrhoea) or to increased metabolic need (growth, pregnancy, lactation, hyperthyroidism). There are numerous single and multivitamin preparations available to provide prophylaxis and therapy. Deficiency of retinol leads to xerophthalmia, squamous metaplasia, hyperkeratosis and impairment of the immune system. Anorexia, skin lesions, hair loss, hepatosplenomegaly, papilloedema, bleeding and general malaise also occur. Chronic overdose also makes the biological membranes and the outer layer of the skin more liable to peel. Therapeutic uses Retinol and derivatives provide therapeutic benefit in a number of clinical areas. Psoriasis Tazorotene, a topical retinoid, is effective in the treatment of chronic stable plaque psoriasis.
Some chemicals antimicrobial countertops discount ofloxacin 400mg without a prescription, called tumor promoters infection on face purchase ofloxacin 200mg overnight delivery, were found effective even when applied to the mouse skin long after a single treatment with a carcinogen applied at a dose too low to give cancer alone infection 6 weeks after c section buy ofloxacin discount. The latter antimicrobial iphone 4 case generic 400 mg ofloxacin overnight delivery, inducing tumors by itself at sufficiently high doses, was a "complete" carcinogen with the salient property of being genotoxic. It is also toxic, killing some cells and thereby stimulating a regenerative response in the surviving basal cells. Tumor promoters are chemicals that do not cause cancer themselves but induce tumor development in skin that has been initiated by a low dose of a carcinogen. Their promoting power generally is parallel to their ability to give sustained hyperplasia of the epidermis with continued treatment. Selective stimulation of tumor growth is envisioned to occur from differential stimulation of initiated cells or due to the insensitivity of initiated cells to toxicity or to terminal differentiation induced in uninitiated cells by the promoter. Continuing efforts to understand the promotion process are envisioned to assist development of short-term tests that predict promoting potential (Curtin et al. An advantage of the experimental model of mouse skin carcinogenesis is the ability to separate the neoplastic process into stages of initiation, promotion, and progression, and the analysis can be extended to more complicated multihit, multistage models (Owens et al. In the simplest model, the skin is treated once with a low dose of an initiator, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, for example. The skin does not develop tumors unless it is subsequently treated with a promoter, which must be applied numerous times at frequent intervals (e. Application of the promoter need not start immediately after initiation, but if it is not continued long enough, or if it is applied before or without the initiator, tumors do not develop. Although an important aspect of promotion is its epigenetic nature, papillomas arising from promotion characteristically are aneuploid. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons A landmark epidemiological investigation by Percival Pott in 1775 connected soot with the scrotal cancer prevalent among chimney sweepers in England. Since that time, substances rich in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (coal tar, creosote, pitch, and soot) have become recognized as skin carcinogens in humans and animals. The polycyclic aromatic compounds alone are relatively inert chemically, but they would tend to accumulate in membranes and thus perturb cell function if they were not removed. They are hydroxylated by a number of cytochrome P450 isozymes, primarily 1A1 and 1B1 in epidermal cells, and conjugated for disposal from the body. Concern persists regarding the use of coal tar for pharmaceutical purposes (Thami and Sarkar, 2004). Repeated treatments are necessary, however, and carry with them an elevated risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer. For example, mice in which the AhR gene has been functionally ablated are insensitive to skin cancer from topical application of benzo(a)pyrene (Shimizu et al. By contrast, a constitutively active AhR expressed in mouse epidermal keratinocytes was not seen to induce neoplasia, but it did result in inflammatory skin lesions reminiscent of contact dermatitis elicited by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in humans (Tauchi et al. Eventually some of the resulting papillomas become autonomous, continuing to grow without the further addition of the promoter. Genetic damage accumulates in the small fraction of tumors that progress to malignancy. A number of natural products are tumor promoters, many of which alter phosphorylation pathways. The best-studied example, and one of the most potent, is the active ingredient of croton oil, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. This is a member of a diverse group of compounds that give transitory stimulation followed by chronic depletion of protein kinase C in mouse epidermis (Fournier and Murray, 1987). Another group of chemicals, an example of which is okadaic acid, consists of phosphatase inhibitors. Compounds acting by other routes are known, including thapsigargin (calcium channel modulator) and benzoyl peroxide (free radical generator). Sensitivity to tumor promotion is an important factor in the relative sensitivity to skin carcinogenesis among different mouse strains and even among other laboratory animal species.
Purchase cheapest ofloxacin and ofloxacin. AgDay: FDA to Phase Out Animal Antibiotics.

In addition antibiotics iv purchase ofloxacin online, many other drugs also cause vascular leasions and toxicity such as bacterial endotoxins and homocysteines antibiotics for sinus infection cipro buy ofloxacin discount, which have unique vascular toxic effects antibiotics for dogs cephalexin purchase genuine ofloxacin on-line. Bacterial Endotoxins Bacterial endotoxins are potent toxic agents to vascular system and cause a variety of toxic effects in many vascular beds virus fall 2014 400 mg ofloxacin for sale. In the liver, they cause swelling of endothelial cells and adhesion of platelets to sinusoid walls. In the lung, endotoxins produce increased vascular permeability and pulmonary hypertension. Infusion of endotoxin into experimental animals produces thickening of endothelial cells and the formation of fibrin thrombi in small veins. The terminal phase of the effects of endotoxin on the systemic vasculature results in marked hypotension. The ability of vitamin E to prevent disseminated intravascular coagulation induced by bacterial endotoxins in the rat suggests that that action of these agents is somehow related to oxidative stress mechanisms. Homocysteine Moderately elevated levels of homocysteine have been associated with atherosclerosis and venous thrombosis. Conditions including increases in the circulating homocysteine involve cardiac complications such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and heart failure. Toxicity may involve oxidative injury to vascular endothelial and/or smooth muscle cells, leading to deregulation of vascular smooth muscle growth, synthesis and deposition of matrix proteins, and adverse effects on anticoagulant systems (Harpel, 1997). This hydrazine derivative causes smooth muscle cell tumors in the aorta and large arteries of mice when administered over the life span of the animals (McManus et al. These tumors have the characteristic appearance and immunocytochemical features of vascular leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas. Smooth muscle cell lysis with vascular perforation apparently precedes malignant transformation. T-2 Toxin Trichothecene mycotoxins, commonly classified as tetracyclic sesquiterpenes, are naturally occurring cytotoxic metabolites of Fusarium species. Intravenous infusion of T-2 toxin in rats causes an initial decrease in heart rate and blood pressure, followed by tachycardia and hypertension and finally by bradycardia and hypotension (Mcmanus et al. Acute T-2 toxin exposure causes extensive destruction of myocardial capillaries, while repeated dosing promotes thickening of large coronary arteries. Vitamin D the toxic effects of vitamin D may be related to its structural similarity to 25-hydroxycholesterol, a potent vascular toxin. The manifestions of vitamin D hypervitaminosis include medial degeneration, calcification of the coronary arteries, and smooth muscle cell proliferation in laboratory animals. Studies have shown that administration of -amyloid produces extensive vascular disruption, including endothelial and smooth muscle damage, adhesion and migration of leukocytes across arteries and venules (Thomas et al. Most importantly, the vascular actions of -amyloid appear to be distinct from the neurotoxic properties of the peptide. The toxic effects of carbon monoxide have been attributed to its reversible interaction with hemoglobin. As a result of this interaction, carboxyhemoglobin decreases the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood, eventually leading to functional anemia. In addition, carbon monoxide interacts with cellular proteins such as myoglobin and cytochrome c oxidase and elicits a direct vasodilatory response of the coronary circulation. Carbon Disulfide Carbon disulfide (dithiocarbonic anhydride) occurs in coal tar and crude petroleum and is commonly used in the manufacture of rayon and soil disinfectants. The mechanism for carbon disulfide-atheroma production may involve direct injury to the endothelium coupled with hypothyroidism, because thiocarbamate (thiourea), a potent antithyroid substance, is a principal urinary metabolite of carbon disulfide. Carbon disulfide also modifies low-density lipoprotein in vitro and enhances arterial fatty deposits induced by a high-fat diet in mice (Lewis et al. Although hemangiosarcomas have also been observed in the liver, lung, and kidney, cardiac tumors are a major cause of death in animals exposed to this chemical. The toxic effects of 1,3-butadiene are dependent on its metabolic activation by cytochrome P450 to toxic epoxide metabolites. The ultimate outcomes of exposure probably are influenced by the rates of glutathione-mediated detoxification of oxidative metabolites. Metals and Metalloids the vascular toxicity of food- and waterborne elements (selenium, chromium, copper, zinc, cadmium, lead, and mercury) as well as airborne elements (vanadium and lead) involves reactions of metals with sulfhydryl, carboxyl, or phosphate groups.
The same group of genotoxicity assays can be used for the collection of both types of information antibiotic 3 times a day purchase ofloxacin 400 mg fast delivery. The advent of molecular biology techniques has certainly aided in the pursuit of mechanisms of mutagenicity and carcinogenicity antibiotics quorum sensing purchase ofloxacin without prescription. It is anticipated that the cancer risk assessment process will evolve as new types of data are obtained virus jumping species safe 200 mg ofloxacin. In this regard infection 2 game cheats cheap ofloxacin online mastercard, some of the issues that remain to be more firmly elucidated are (1) the relative sensitivities of different species (particularly rodent and human) to the induction of organ-specific mutations and tumors by chemicals and radiation; (2) the shape of the dose response for genetic alterations and tumors at low (environmental) exposure levels, especially for genotoxic chemicals; and (3) the relative sensitivity of susceptible subpopulations of all types. A better understanding of these major issues will greatly reduce the uncertainty in cancer risk assessments by, in part, replacing default options with biological data. A particular MoA can further be defined by a set of key events that are required for tumor development (Preston and Williams, 2005). In addition, the key events can be used to establish whether or not a particular MoA described for a rodent model is plausible in humans (the so-called Human Relevance Framework, Meek et al. This more defined approach based on the use of the best available science can possibly be extended to include noncancer health effects (Seed et al. Data obtained for genetic alterations in rodent somatic and germ cells and human somatic cells are used to estimate the frequency of the same genetic alterations in human germ cells. The final step is to estimate the frequency of these genetic alterations that are transmitted to offspring. Genetic Risk Assessment the approach for conducting a genetic risk assessment is less well defined than that for cancer risk. An in-depth discussion of the topic can be found in the book Methods for Genetic Risk Assessment (Brusick, 1994). These two articles serve to highlight the difficulties with and uncertainties in genetic risk assessments. The general approach is to use rodent germ cell and somatic cell data for induced genetic alterations and human data for induced genetic alterations in somatic cells (when available) to estimate the frequency of genetic alterations in human germ cells. The aim of this approach is to develop two sensitivity factors: (1) somatic to germ cell in the rodent and (2) rodent to human using somatic cells. These factors can then be used to estimate genetic alterations in human germ cells. In addition, separate genetic risk assessments need to be conducted for males and females, given the considerable difference in germ cell development and observed and predicted sensitivity differences. However, much greater detail can be found in recent reviews that are referenced at the appropriate places within each section. In addition, it has been reported more recently that multiply damaged sites or clustered lesions can be formed that appear to be more difficult to repair. Such lesions consist of multi single lesions, including oxidized purine or pyrimidine bases, sites of base loss, and single-strand breaks. For example, single-strand breaks and base damages predominate with X-rays, for which ionization density is sparse, whereas the frequencies of single- and double-strand breaks are more similar with alpha particles, for which ionization density is dense. The frequencies of individual base damages have been assessed using monoclonal antibodies, for example (Le et al. Ultraviolet Light Ultraviolet light (a nonionizing radiation) induces two predominant lesions, cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers and 6,4-photoproducts. In part because of this feature, the repair of cyclobutane dimers and 6,4-photoproducts has been extremely well characterized, as discussed below. For example, the alkyl group of an N7-alkylguanine adduct, which is a major adduct formed by many alkylating agents, labilizes the bond that connects the base to deoxyribose, thereby stimulating base loss. Such adducts can also hinder polymerases and cause mutation as a consequence of errors that they trigger in replication. The size of the gap is dependent upon the particular polymerase involved in the repair. Oxidative damage, either background or induced, are important substrates for base excision repair (Lindahl, 2000). The basic steps are damage recognition, incision, excision, repair synthesis, and ligation.