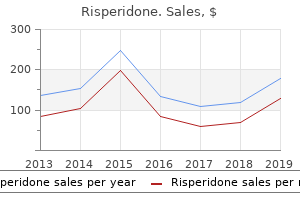
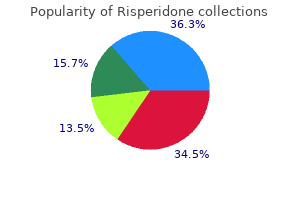
Risperidone
"Generic risperidone 2mg overnight delivery, medications known to cause pill-induced esophagitis".
By: P. Umbrak, M.B.A., M.D.
Vice Chair, Columbia University Roy and Diana Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons
Childhood maltreatment histories facial treatment cheap risperidone online amex, alcohol and other drug use symptoms symptoms 3 days before period buy generic risperidone, and sexual risk behaviours in a treatment sample of adolescence symptoms nervous breakdown order 2 mg risperidone amex. Panama Goverment: National Plan of Action of the Childhood and the Adolescence (2007) treatment hepatitis b order risperidone online from canada. Thesis "Diagnosis of prevalence of licit psychoactive substances (alcohol and tobacco) in male and female students 16-45 years of age,who are between the first and fifth years of study during cycle 01 of the year 2004". Estudio comparative entre estudiantes de dos Facultades de Medicina en Nicaragua sobre la prevalencia del uso de drogas y otros aspectos relacionados, durante el period de Noviembre 2008 y Enero 2009. Childhood maltreatment linked to greater symptom severity and poorer quality of life and functional in social anxiety disorder. Concomitance between childhood sexual and physical abuse and substance use problems: A review. Testing the interaction between parent-child relationship factors and parent smoking to predict youth smoking. Gender differences in victimization severity and outcomes among adolescents treated for substance abuse. The casual impact childhood-limited maltreatment and adolescent maltreatment on early adult adjustment. Canadian Incidence Study of Reported Child Abuse and Neglect-2003: major findings. Religiosity and substance use: test of an indirect effect model in early and middle adolescence. Parental modeling and parental behavior effects on offspring alcohol and cigarette use: A growth curve analysis. Role of parent support and peer support in adolescent substance use: A test of mediated effects. A prospective examination of the path from child abuse and neglect to illicit drug use in middle adulthood: the potential mediating role of four risk factors. We described, analyzed and discussed the incidence, lifetime prevalence and other time prevalence of the use of licit and illicit drugs. We also looked at the proportion of students who had experienced psychological distress and/or maltreatment during childhood. Taking the theoretical assumptions of a bio ecological perspective on human development for the analysis and discussion of the findings, the study explored whether or not there was a relationship between the use of psychoactive substances and the variables of psychological distress and child maltreatment. Justification It is widely recognized that the use of alcohol and other licit and illicit drugs is an international public health problem, which may be approached from different perspectives. Forty million children under the age of 15 in Latin America and the Caribbean experience violence, abuse and abandonment in the family. Marijuana was the illicit substance that was most used, with lifetime prevalence of 8%. It was also reported that young adults between the ages of 18-24 had the highest level of alcohol use, with a rate of 46%, followed by the 25-34 age group, at 43%. The present research examined the relationship between drug use by undergraduate students in two universities in Colombia and maltreatment during childhood (physical, sexual or psychological abuse, or emotional or physical abandonment). Methodology this exploratory study was cross-sectional in nature, and collected retrospective information from the student population on psychoactive substance use and maltreatment during childhood (physical, sexual or psychological abuse or neglect). In terms of the sample, in the private university in Bogota, male and female university students over the age of eighteen who were enrolled as undergraduates were chosen in a non-stratified random sample. Student from 18 faculties in courses selected at 95 random in each faculty were surveyed, on a voluntary basis. In the university in Villavicencio, the sample was drawn by means of a randomized probability method.
In addition medicine 4 the people cheap risperidone 4mg, this guideline will be the first to address the subtype of Complement-mediated diseases treatment cervical cancer generic risperidone 3mg on line. Each chapter follows the same template providing guidance related to Diagnosis symptoms 6 year molars buy risperidone american express, Prognosis treatment ingrown toenail order 2 mg risperidone overnight delivery, Treatment, and Special situations. The goal of the guideline is to generate a useful resource for clinicians and patients by providing actionable recommendations with useful infographics based on a rigorous formal literature systematic review. Another aim is to propose research recommendations for areas where there are gaps in knowledge. Limitations of the evidence are discussed, with areas of future research also presented. In most end-stage kidney disease registries, glomerular diseases account for about 20% to 25% of the prevalent cases. In this guideline, we have largely maintained the topics covered in the first edition, focusing on the most common adult and pediatric glomerulonephritides. Consistent with new findings on disease pathogenesis, the updated Membranous Nephropathy chapter now provides an in-depth discussion of monitoring pathogenic autoantibodies in disease management. The chapter on Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis compares and contrasts B-cell targeted therapies with traditional cytotoxic drugs. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children takes advantage of several new trials that have defined duration of immunosuppression, and this chapter has been written to closely align with recommendations from the International Pediatric Nephrology Association. The guideline primarily considers questions of clinical management for which high quality scientific evidence is available. Rather, in collaboration with an Evidence Review Team, the Work Group reassessed questions posed in the 2012 guideline version and identified several issues that have remained clinically pressing and for which there is now at least some evidence base to make defensible recommendations. At the end of each chapter, a research agenda has also been included and is intended to provide a roadmap for future investigation based on our comprehensive review of the current state of clinical evidence. Given this situation, evidence-based recommendations have been supplemented with practice points, based on retrospective analyses, registry data, and consensus of expert opinion to fill in management gaps when there was insufficient evidence to make a formal recommendation. The reader will notice that most of this guideline is comprised of practice points. This should be taken as a challenge to the clinical investigators of the nephrology community to develop novel clinical trial designs, such as basket trials, umbrella trials, biomarker-driven trials, and n-of-one trials, to implement the proposed research agenda in the absence of a sufficient number of patients to carry out traditional prospective randomized controlled trials. The Work Group was diverse, multinational, multidisciplinary, experienced, thoughtful, and dedicated, and volunteered countless hours of their time developing this guideline. The kidney biopsy is the "gold standard" for the diagnostic evaluation of glomerular diseases. However, under some circumstances, treatment may proceed without a kidney biopsy confirmation of diagnosis. Repeat kidney biopsy should be performed if the information will potentially alter the therapeutic plan or contribute to the estimation of prognosis. Full anticoagulation is indicated for patients with thromboembolic events occurring in the context of nephrotic syndrome. Its value is unknown for patients with nephrotic syndrome due to other underlying diseases Albumin value of 2. In the absence of visible hematuria and when reversible causes have been excluded. Other biomarkers may not be available in all centers; this table provides an overview of useful biomarkers. In patients who do not tolerate or can no longer use cyclophosphamide, consultation with an expert center is advised. The course may be less well-defined or more difficult to interpret in many patients. B-cell depletion is insufficient to judge the efficacy of rituximab therapy; extra doses may be considered even if B-cells in the peripheral blood are absent or very low. Management of initial relapse after therapy *The definition of relapse is variable. In patients with a partial remission (characterized by normalization of serum albumin), a relapse should be defined by an increase of proteinuria paralleled by a decrease in serum albumin levels. In patients with very early relapse, it is important to consider reasons for the failure of the previous therapy. Cyclophosphamide treatment should take into account the maximal tolerable dose: the cumulative dose should not exceed 10 g if preservation if fertility is required. When considering anticoagulant therapy, it is important to balance benefits and risks.
However medications hyponatremia cheap risperidone 2mg otc, within the past few years ok05 0005 medications and flying cheap 4 mg risperidone with mastercard, observational studies have demonstrated that non-immunological factors medications pregnancy discount 3 mg risperidone mastercard, such as proteinuria and higher blood pressure medications causing hair loss buy risperidone 4 mg on line, appear to be risk factors in diseases of transplanted as well as native kidneys. However, few patients with chronic kidney disease have been included in population-based epidemiological studies of cardiovascular disease or long-term, randomized clinical trials. In general, the Task Force concluded that most interventions that are effective in the general population should also be applied to patients with chronic kidney disease. In addition, other professional organizations are focusing on other risk factors or other target populations. Evidence model for stages in the initiation and progression of cardiovascular disease, and therapeutic interventions. Thick arrows between ellipses represent factors associated with initiation and progression of disease that can be affected or detected by interventions: susceptibility factors (black); initiation factors (dark gray); progression factors (light gray); and end-stage factors (white). A systematic search yielded few guidelines for diagnosis and management of earlier stages of chronic kidney disease (Table 7). In addition, standards of care have not been defined in a universally accepted format. Therefore, there is no ongoing effort to ascertain adherence to standards for care or outcomes for patients with earlier stages of chronic kidney disease. However, even in the absence of such studies, there is substantial evidence of ``under-diagnosis' and ``under-treatment. Thus, neither elderly diabetic nor hypertensive patients, who are at increased risk for chronic kidney disease, were adequately evaluated or treated with proven agents. Among patients beginning peritoneal dialysis, 42% had severe anemia, 27% were referred to a nephrologist late, and 19% initiated dialysis with very low levels of kidney function. These are but a few examples from a literature replete with evidence of inadequate diagnosis and treatment of earlier stages of chronic kidney disease, even though appropriate interventions have been shown to improve outcomes. Overall, these findings suggest that diagnosis and treatment in the community fall far short of the few recommended guidelines that have been developed. This review will provide a detailed framework for the questions the Work Group chose to ask (Table 8). Prevention requires a clear understanding of prevalence and outcomes of disease, earlier stages of disease, antecedent risk factors, and appropriate treatments for populations at risk. There is a spectrum of risk for adverse outcomes, ranging from ``very high risk' in those with the disease, to ``high risk' in those with risk factors for developing the disease, to ``low risk' for those without the disease or its risk factors. The population as a whole includes many more individuals at low risk than at high risk. Public health measures addressing chronic diseases include strategies to prevent adverse outcomes in individuals at very high risk and high risk, as well as widespread adoption of life-style modifications to reduce the average risk profile of the population. With regard to risk stratification for adverse outcomes from chronic kidney disease, patients with chronic kidney disease would be included in the ``very high risk' group. The risk of adverse outcomes in chronic kidney disease can be further stratified by the severity of disease and rate of progression. Therefore, for most patients, the risk of adverse outcomes tends to increase over time. The major task of the Work Group was to develop ``A Clinical Action Plan'-an approach to chronic kidney disease that relates stages of severity of chronic kidney disease to strategies for prevention and treatment of adverse outcomes. To accomplish this task it was first necessary to outline the conceptual approach, including operational definitions of chronic kidney disease and the stages of severity of chronic kidney disease; determination of the prevalence of chronic kidney disease; issues in the evaluation and management of various types of chronic kidney disease; definition of individuals at increased risk of chronic kidney disease; definition of outcomes of chronic kidney disease; association of complications of chronic kidney disease with decreased kidney function; modalities of kidney replacement therapy; and an approach to chronic kidney disease using the guidelines. Public Health Problem 29 disease, nor is there reliable information on the prevalence, treatment patterns, outcomes, and cost of these earlier stages, nor information on how many people choose to forego dialysis and transplantation despite kidney failure. Risk factors for the development of chronic kidney disease have not been well described, and there is no reliable estimate of the size of the population at risk. This section introduces the rationale for developing a definition of chronic kidney disease and classification of stages of severity; risk factors for adverse outcomes of chronic kidney disease; the relationship between disease severity and rate of progression as risks for adverse outcomes; the definitions and stages defined by the Work Group; and laboratory tests for the detection of each stage. More reliable estimates of the prevalence of earlier stages of disease and of the population at increased risk for development of chronic kidney disease; 2. Recommendations for laboratory testing to detect earlier stages and progression to later stages; 3. Evaluation of factors associated with a high risk of progression from one stage to the next or of development of other adverse outcomes; 5. Defining chronic kidney disease and stages of severity requires ``categorization' of continuous measures of markers of kidney damage and level of kidney function.
The term does not apply to brain injuries that are congenital or degenerative symptoms internal bleeding generic risperidone 3 mg free shipping, or to brain injuries induced by birth trauma symptoms 9 days after embryo transfer discount risperidone 4 mg with amex. The standards for determining employment discrimination under the Rehabilitation Act are the same as those used in Title I of the Americans with Disabilities Act treatment ingrown hair generic 4mg risperidone amex. Because of the range of systems affected symptoms vaginal cancer buy discount risperidone 3mg on line, management requires a more expansive approach than most disorders and care is best provided by a coordinated, multidisciplinary team. Affected children are unable to complete tasks and follow directions in the same way as neurotypical children. Affected children (and their families) may cycle through the stages of grief (denial, anger, bargaining, depression, and acceptance) as their disease progresses. Emotional and behavioral reactions may increase with an increase in physical and cognitive symptoms due to disease progression, and when affected individuals feel stuck because of their disease in comparison to their unaffected peers. Affected children may experience feelings of anxiety, hostility, depression and apathy, and may exhibit behaviors such as passivity or tantrums. When addressing psychosocial concerns, it is important to respond as you would to any child having an emotional reaction to change and/or circumstances. Working together to openly address emotions provides learning opportunities for affected children and parents/caregivers to engage in active listening, increase awareness of emotions and associated behaviors, and to problem solve. Planning activities that affected children can successfully complete creates a positive experience that may increase sense of control, motivation to continue, and healthy coping strategies. The systems affected, the severity of symptoms, and the age of onset of those symptoms vary greatly between individuals, even in the same family. Symptoms tend to worsen gradually over several decades, though symptoms worsen at a different pace for different people. While no treatment currently exists that slows the progression of myotonic dystrophy, management of its symptoms can greatly improve patient quality of life. In the most severe cases, respiratory and cardiac complications can be life-threatening even at an early age. In general, the younger an individual is when symptoms first appear, the more severe symptoms are likely to be. However, how myotonic dystrophy affects one individual can be completely different from how it manifests in another, even for members of the same family. Prognosis is as variable as the symptoms of this disease, thus it is difficult to make an accurate prognosis due to varied progression. Appropriate amounts of fiber supplements may be useful, although overuse may produce impaction if the patient becomes constipated. Swallowing problems come from both oropharyngeal muscle weakness and abnormal motility of the esophagus. The patient should be evaluated by a speech pathologist and a gastroenterologist with fibroscopic and manometric testing. If patients are not able to do these studies, the modified barium swallow test should be done to assess the risk for aspiration. The speech therapist should be able to give useful advice to alleviate the problem. If the problem imposes high aspiration risks, G tube insertion should be considered. If aspiration occurs, or may have occurred and fever starts, go to an emergency center for treatment. Overdoing is counter-productive, thus low intensity aerobic training may be useful, such as resistive exercises in water. Modafinil is a common choice although it is expensive, but can often by covered by insurance when documentation meets the requirements. Some children with significant learning or emotional needs can engage in challenging behavior when they are upset or angry.
Standard Treatment Guidelines and Essential Drugs List for South Africa: Hospital Level paediatrics symptoms 8 weeks pregnant order cheap risperidone online. Improving the quality and timeliness of care is a critical step to save these lives medications pictures buy risperidone 2mg cheap. These Newborn Care Charts for Management of Sick and Small Newborns in Hospital are designed to be used by doctors and nurses at the district and regional hospital level and provide a ready reference for assessment treatment neuroleptic malignant syndrome buy cheap risperidone 3 mg on-line, classification symptoms 5 weeks pregnant cramps discount risperidone 2 mg on line, and treatment of sick and small newborns as well as an overview of routine care that should be provided to all newborns. Produced in collaboration with the Ethiopia Public Health Training Initiative, the Carter Center, the Ethiopia Ministry of Health, and the Ethiopia Ministry of Education. Important Guidelines for Printing and Photocopying Limited permission is granted free of charge to print or photocopy all pages of this publication for educational, not-for-profit use by health care workers, students or faculty. All copies must retain all author credits and copyright notices included in the original document. Under no circumstances is it permissible to sell or distribute on a commercial basis, or to claim authorship of, copies of material reproduced from this publication. Except as expressly provided above, no part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without written permission of the author or authors. This material is intended for educational use only by practicing health care workers or students and faculty in a health care field. Moreover it is rapidly evolving and one needs periodic updating and catching up with the state of the art knowledge. Providing a comprehensive review of internal medicine is not only difficult but almost impossible, as the field is vast and extensive. Despite this limitation, the authors have tried to provide a basic framework for working knowledge of Internal medicine. Even though a number of individuals have contributed in the original document of this lecture note, as more than 3 years have elapsed, most of the topics are reviewed, and some topics are completely rewritten, to include new developments and the state of the art scientific knowledge. This lecture note has been written primarily for Health officer students; however it can also be used by medical students and all other health science students who deal with patients, who have medical illnesses. Our special thanks go to the contributing authors, who took time from their very tight schedules, to prepare the draft lecture notes, in different topics. We sincerely appreciate the effort of the reviewers who have given their valuable comments and inputs during the initial within University review, and the subsequent joint reviews conducted at the Carter center, in Addis Ababa. Akilu Azaje, Assistant professor of Internal medicine, in the department of Internal Medicine at the Medical faculty of Addis Ababa University, who has reviewed the first draft lecture note, for his guidance and outstanding comments and valuable inputs. We also thank all the staff of the Carter center, Ethiopia for their hospitable hosting and assistance during the development of the lecture note. Last but not least our deepest gratitude extended to Ato Aklilu Mulugeta, for his tremendous effort, close follow-up and contribution in facilitating the completion of this lecture note. Associate professor of Internal medicine, Faculty of Medical sciences, Jimma University Zenebe Assefa, M. Assistant professor of Internal medicine, Faculty of Medical sciences, Jimma University Abera Bekele, M. Assistant professor of Internal medicine, Faculty of Medical sciences, Jimma University Diseases of the Kidneys Diseases of the Nervous system Chapters or Topics contributed Infectious diseases Diseases of Metabolism and the Endocrine System Diseases of the connective tissue and Joints Diseases of the Nervous system Diseases of the Cardiovascular system Infectious diseases Diseases of the Respiratory system Diseases of the Gastrointestinal system Hematologic diseases Diseases of Metabolism and the Endocrine System iii Woldecherkos Abebe, M. Assistant professor of Internal medicine, Faculty of Medical sciences, Jimma University Fetih Mohammed, M. Assistant professor of Internal medicine, Health sciences Faculty, Jimma University Tesfaye H/ Tsion M. Lecturer in the department of Internal medicine, Faculty of Medical sciences, Jimma University Girma Tesfaye, M. Other connective tissue diseases: Systemic Sclerosis, Mixed connective tissue disorders. Introduction to infectious diseases Generally infectious diseases result from bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Despite decades of dramatic progress in their treatment and prevention, infectious diseases remain a major cause of death and are responsible for worsening the living conditions of many millions of people around the world especially in the developing countries. Infectious diseases often do not occur in isolated cases; rather they spread through a group exposed from a point source.
Order 2mg risperidone free shipping. I have a mental illness let me die - BBC Stories.