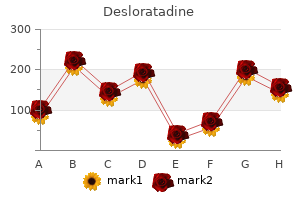
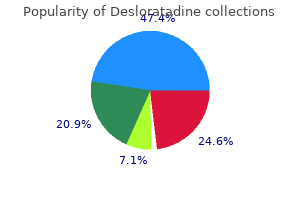
Desloratadine
"Cheap desloratadine 5 mg on line, allergy treatment emergency".
By: R. Altus, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, Kaiser Permanente School of Medicine
The child is completely stripped and in the vertical position allergy treatment for 3 month old order genuine desloratadine online, the Levels of the thigh folds studied allergy shots make you gain weight cheap desloratadine 5 mg without prescription. Normally allergy symptoms or cold buy desloratadine 5 mg on-line, the head lies in the lower and inner quadrant formed by these two lines allergy over the counter purchase generic desloratadine canada. In addition, patient will have features of secondary osteoarthritis of the hip namely pain, stiffness, limp, crepitus, restricted movements, etc. The methods to obtain reduction of the head into the acetabulum vary according to the age groups (Table 35. In infants Reduction can be obtained and maintained by Pavlik harness, which was first described by Arnold Pavlik, in the former Czechoslovakia, in the year 1958, von Rosen splints and other splints. This is the only harness that promotes spontaneous reduction of a dislocated hip and maintains the reduction, whereas other appliances only maintain the reduction. Apart from the reduction and the immobilization, it allows active movements in all directions except extension and adduction. Later wean, by removing it 2 hours/day doubled every 2-4 weeks until device is worn in the night only. X-rays are taken at 1 month 6 months 1 year intervals If dislocation persists for 6-8 weeks, abandon this program and institute · Traction · Closed reduction · Casting 618 months Pull and hold in this age group harness is not successful. The recommended regime as follows: · Preoperative traction · Adductor tenotomy · Closed reduction and arthrogram. Toddler (18-36 months) Break and hold Child (3-8 years) Open and break 499 Juvenile and young adults (8-18 years) Open and replace Depending on the situation, the following procedures are chosen: · Femoral shortening with pelvic osteotomy. Useful between 18 months and 6 years · Pemberton Uses triradiate cartilage as the hinge. Here, the treatment of choice is gentle closed reduction and 500 General Orthopedics hip spica application. It is an anteroposterior view of the pelvis taken with the lower limbs in full medial rotation and 45° abduction. When the hip is normal, upward prolongation of the long axis of the shaft of the femur points towards the lateral margin of the acetabulum and crosses the pelvis in the region of the sacroiliac joint. When the hip is dislocated upward, prolongation of this line points towards anterior iliac spine and crosses the midline in the lower lumbar region. Between 18 and 36 Months In this age group, open reduction is the treatment of choice as closed reduction is often not successful. Open reduction is to be followed with either pelvic or femoral osteotomy to provide concentric reduction of the femoral head within the acetabulum. Role of osteotomies: Osteotomies are done for instability, failure of acetabular development or progressive head subluxation after reduction. They are done only if congruent reduction is possible, if there is satisfactory range of movements and if the femoral head has a reasonable sphericity. The osteotomies could be femoral or pelvic and the choice is usually left to the surgeons, but there are some guiding principles. Pelvic osteotomies: these are chosen if there is severe dysplasia and if radiographic changes are seen on the acetabular side. Femoral osteotomies: this is the procedure of choice if there are changes in the femoral head and if there is increase in anteversion of the neck. If osteoarthritis of the hip develops, total hip replacement is the surgery of choice. The procedure consists of using the symphysis pubis as a hinge, osteotomizing the acetabulum to cover the head. Here, the osteotomy is done through the acetabular roof using triradiate cartilage as the hinge. Here, the osteotomy is done through the ilium above the acetabulum and the distal fragment is pushed medially. Quadriceps contracture or congenital absence or hypoplastic anterior cruciate ligament. Pathology Varies with severity but anterior capsule and quadriceps are contracted. There are always intraarticular adhesions, hypoplasia or absence of patella or lateral dislocation of patella, and hypoplastic vastus lateralis. Clinical Features the patient presents with hyperextension deformity of the knee and could be quite grotesque. Treatment Mild to Moderate In these cases, conservative methods like Pavlik harness, serial casting and skeletal traction are the treatment of choice.
Case 4266 had a classic two-point discrimination of 4 mm (thumb) and 12 mm (index) and could pull the correct coins from his pocket allergy testing gold coast bulk bill discount 5mg desloratadine mastercard. Porter12 studied fingertips resurfaced with flaps and grafts allergy medicine in pregnancy buy desloratadine 5 mg online, comparing sensibility tests with hand function allergy symptoms of peanut butter cheap 5mg desloratadine with amex. In another correlation of sensibility tests and hand functions done on patients with flaps (neurovascular island flaps) allergy forecast chicago purchase desloratadine 5 mg online, Krag and Rasmussen13 noted that patients had the ability perform the pick-up test yet had poor two-point discrimination. There has been a recent study on end-results after nerve injury that also attempted to relate sensibility testing to hand function. Although with a Weber test of 16 mm or less, he identified most of the objects correctly, he could also identify some objects when he had effectively no classic two-point discrimination. These types of observations, as discussed in Chapter 8, were part of the stimulus that led me to develop the moving two-point discrimination test. The study did graphically contrast results of von Frey hairs (Semmes-Weinstein monofilaments) with results of the classic Weber two-point discrimination. Furthermore, for two-point discrimination values in the 6- to 12 mm range, in which, according to Moberg, tactile gnosis should still be possible, there were many patients with abnormal von Frey values. This "plastic ridge device" gave values which correlated with neither von Frey hair nor Weber test results. I have explained17 these findings in light of the neurophysiologic principles discussed in Chapter 3. The Plastic Ridge Device is testing the quickly-adapting while von Frey and Weber test the slowly-adapting fiber/receptor populations. As discussed in Chapter 8, the Ridge Device is not only based on inappropriate philosophical speculation (there is no somatic senses of space or choraesthesia), but also is poorly calibrated, has a wide range of normal, is difficult to use, and so, is difficult to obtain. They failed to correlate Ridge results with either the pick- up or object identification test, so they cannot make a valid correlation of Ridge results with tactile gnosis. The importance of their work is the further confirmation that tests of threshold (von Frey) do not necessarily correlate with tests of innervation density. In a given test area the threshold for perception of constant-touch/pressure can be normal if just one slowly-adapting fiber reinnervates the appropriate Merkel cell-neurite complex and this has had time to "mature" prior to testing. In an adjacent area this reinnervation may not have occurred, and the threshold would be abnormal (higher). I believe the slowly-adapting fiber/receptor system is predisposed for this to occur following nerve repair for three reasons: (1) the Merkel cell-neurite complex degenerates more rapidly than its quickly-adapting fiber/receptor system counterpart (see Chapter 4). Therefore, there will be less Merkel cells in an optimal state for reinnervation by the regenerating axon; (2) the ratio of axon to corpuscle in this system is less than one (Merkel cellneurite complex: <1, Pacinian corpuscle: 1, Meissner corpuscle >1, see. Therefore, the chances of a Merkel cell being reinnervated by a regenerating axon is the least likely of the sensory corpuscular endings; and 3) the slowly-adapting fibers comprise only about one-third of the group A beta fibers (see Chapter 3). Therefore, if only a fraction of the proximal axons re-enter distal endoneurial sheaths, and if only a fraction of these are correctly redirected, i. To restate this thesis: regeneration favors recovery in the quickly-adapting Meissner afferent system, the system for movement detection. Delivering the first Sterling Bunnell Memorial Lecture before the American Society for Surgery of the Hand in 1964, he said18 "The tools are still crude and must be improved. Good results in the laboratory (clinical examination) can be useless in life and vice versa. Patients listed decreased thumb motion highest as the cause of decreased usefulness of their replanted thumb (Table 10. The authors concluded "that greater than 10 mm or two-point discrimination is compatible with good sensation: and that these findings indicate that "motion, as well as sensibility, is important in the replanted thumb. This evaluation included moving and constant-touch, 30and 256-cps vibratory stimuli, classic and moving two-point discrimination, vibratory, (Biothesiometer) and cutaneous pressure (Semmes-Weinstein monofilaments) thresholds, and a timed pick-up (sighted) and object recognition (blindfolded) test. The results demonstrated that tactile gnosis begin to recover when the moving two-point discrimination is less than 7 mm, a time during recovery from nerve re pair when classic two-point discrimination is usually greater than 15 mm (see Table 10. This study22 demonstrated for the first time the functional difference between a recovered peripheral innervation densities of the group A beta fiber subpopulations. Among the patients studied were those following nerve repair who had recovered to the point where they could perceive constanttouch, had wide ranging cutaneous pressure thresholds, and two-point discrimination greater than 15 mm. They could perceive moving-touch had near normal vibratory twopoint discrimination threshold at 120-cps, and moving two-point discrimination between 4 and 6 mm. I found that they could easily identify objects placed between their thumb and index finger if they moved the object between their fingers (Table 10.

You and your patients should anticipate this and use supports that are meaningful to your patients allergy symptoms dogs eyes order cheap desloratadine. In motivated patients allergy shots lightheadedness purchase cheap desloratadine online, a slow-down of the tapering process may be necessary toward the end allergy forecast oklahoma desloratadine 5 mg mastercard. Discontinuation Strategies Two strategies that can be used to taper off of benzodiazepines: 1 allergy shots grand rapids mi buy line desloratadine. Simultaneous treatment with an anti-epileptic drug during taper; this allows for a more rapid taper. Special Circumstances Consider inpatient/medical residential treatment in patients with significant substance abuse history, history of benzodiazepine overdose, seizure disorder or illicit benzodiazepine use. Calculate the dose equivalence of the current benzodiazepine into clonazepam, diazepam, or phenobarbital long-acting drug. Provide behavioral support to the patient during the tapering process above (see General Considerations concerning opioid tapering). Be conservative in estimating the long-acting dose since variation in metabolism may create safety issues. See the patient for a return visit a few days after initiating the taper to be sure your dose equivalency is appropriate. Reduce the total dose of the long-acting agent by 510% per week in divided doses. Consider slowing the taper to 5% or less per week when the dose has been reduced to 25 50% of the starting dose. Consider adjunctive agents to help with symptoms: trazodone, buspirone, antidepressants, hydroxyzine, clonidine, neuroleptics and alpha-blocking agents have all been useful. Benzodiazepine Equivalency Chart Drug Chlordiazepoxide (Librium) Diazepam (Valium) Flurazepam (Dalmane) Phenobarbital (barbiturate) Alprazolam (Xanax) Clonazepam (Klonopin) Lorazepam (Ativan) Oxazepam (Serax) Temazepam (Restoril) Triazolam (Halcion) Action Onset Int Rapid Rapid Slow Peak Onset (hrs) 24 1 0. Iowa Pain Management Toolkit 52 Benzodiazepine Tapering Flowsheet Start Here Consider benzodiazepine taper for patients with aberrant behaviors, behavioral risk factors or concurrent opioid use. Switch from short-acting agent (alprazolam, lorazepam) to longer acting agent (diazepam, clonazepam, chlordiazepoxide or phenobarbital). Upon initiation of taper, reduce the calculated dose by 25 50 percent to adjust for possible metabolic variance. Schedule first follow-up visit two to four days after initiating taper to determine if adjustment in initial calculated dose is needed. After 1/4 to 1/3 of the dose is reached, you can slow the taper with cooperative patient. With cooperative patients who are having difficulty with this taper regimen, you can extend the total time of reduction to as much as six months. Consider adjunctive agents to help with symptoms: trazodone, hydroxyzine, neuroleptics, anti-depressants, clonidine and alpha-blocking agents. Drug Chlordiazepoxide (Librium) Diazepam (Valium) Alprazolam (Xanax) Clonazepam (Klonopin) Lorazepam (Ativan) Oxazepam (Serax) Triazolam (Halcion) Phenobarbital (barbituate) Half-Life (hrs) 5 30 h 20 50 h 6 20 h 18 39 h 10 20 h 3 21 h 1. Follow the usual safegards (lab testing and blood levels) when prescribing these medications. Use adjuvant medications as mentioned above for rebound anxiety and other symptoms. Iowa Pain Management Toolkit 53 Specialty Care for Chronic Pain Pain is an aspect of many illnesses, as well as a normal part of the aging process. The treatment of pain, especially acute pain, may at times require the use of opioids, which have significant risks in addition to their benefits. After years of misguided provider education, millions of patients in our healthcare system are on opioids for inappropriate diagnoses and at inappropriate doses. Even the most skilled providers may at times need specialty care to assist in the management of these complex patients. This guideline will address the following questions: What kinds of patients are most appropriate for specialty care? What kind of oversight should exist to assure consistent and safe management of these patients? Respiratory: S T O P B A N G or similar, with appropriate referral or further evaluation as necessary. Evaluation for possible unforeseen sources of nociception, such as identification of ongoing tissue destruction. Iowa Pain Management Toolkit 54 Oversight Pain specialists accredited, or working under the license of others can succumb to lack of time and inadequate resources resulting in a loosening of appropriate safeguards in the management of chronic pain.
Let us approach the subject of modern witchcraft neither in a spirit of incredulity nor of superstition allergyworx discount 5mg desloratadine with mastercard, but from the standpoint of the psychologist allergy testing colorado springs cheap desloratadine 5mg fast delivery, seeking to understand the workings of the mind and prepared to discover much that had hitherto passed unsuspected allergy medicine kroger best 5mg desloratadine. One of the most common eye problems to present to health workers is acute red eye(s) allergy medicine epinephrine buy generic desloratadine from india. Approximately 40% of all outpatients seen in Bawku, Ghana, and in ten district hospitals in Pakistan, present with red eyes (Figure 1). While the more serious causes of red eye need prompt recognition and management by an eye specialist, in many cases red eye can be managed at the first point of health care (primary level). If primary health care workers are able to differentiate the various causes of red eye and provide primary level treatment, there are two important advantages: · Patients are managed quicker and care workers closer to where they live examine a baby. This issue of the Community Eye Health Journal gives an overview of what the primary level health care worker can do for patients presenting with red eye. We have limited this to non-traumatic causes, as eye injuries will be discussed in a separate issue of the journal later this year. We also include useful summary diagnostic and management tables and a quiz that can be used for training primary level eye care workers. Please send details of your name, occupation and postal address to Community Eye Health Journal, at the address above. The red eye forms a big proportion of the eye problems seen in most eye clinics in developing countries. For example, in the Bawku Hospital eye unit, Ghana, in 2004 a total of 21,391 patients were seen as outpatients, out of which 8,931 were red eyes of one type or another, representing over 40% of the total number of patients screened. The majority of red eyes are seen at community clinics and health centres, where diagnosis and management are done by community health nurses, primary eye care workers and ophthalmic nurses. It is for this reason that adequate attention should be given to the prevention, early diagnosis and first aid management of these conditions. The common causes of acute red eye are conjunctivitis and trachoma, corneal ulcer, acute iritis, acute glaucoma and injury (or trauma). Red eye may also be due to the use of harmful traditional medicines for other eye conditions. This article deals mainly with first aid (primary level) management of red eye, which is not due to an injury. Allergic conjunctivitis (sometimes called vernal conjunctivitis or vernal keratoconjunctivitis) usually has a long history of intense itching of both eyes. In very severe cases these children will need topical steroids prescribed by a specialist. Steroid eye preparations can be dangerous and should only be prescribed by an eye specialist. Conjunctivitis of the newborn Any eye infection in the first 28 days of life is known as neonatal conjunctivitis or ophthalmia neonatorum. The eyelids are very swollen and pussy, the conjunctiva is red and may be blood stained, the cornea is usually clear (but a white spot on it could be an ulcer which is serious and needs urgent referral). Management Clean the eyes gently with clean water or normal saline and apply tetracycline ointment hourly. If the cornea is involved, refer to an eye centre where the baby will be treated with intensive antibiotic eye drops and, sometimes, systemic antibiotics. Prevention All babies should have their eyes cleaned immediately after birth, and tetracycline ointment applied. Educate traditional birth attendants, community health workers, and both parents as this is often a sexually transmitted disease. Conjunctivitis Conjunctivitis affecting all ages this is the most common cause of red eye. There are different types of conjunctivitis: bacterial conjunctivitis caused by a bacterium. The signs vary depending on the cause but include swollen eyelids, red conjunctiva and a watery or pussy discharge. To treat bacterial conjunctivitis, clean the eyes and apply any topical antibiotic. In the absence of any antibiotics, merely cleaning the eyes of discharge regularly will allow the eyes to settle in a few days. Usually no treatment is required for viral conjunctivitis but an antibiotic ointment can reassure the patient.
Desloratadine 5mg line. Eye Strain - Causes Symptoms Relief.