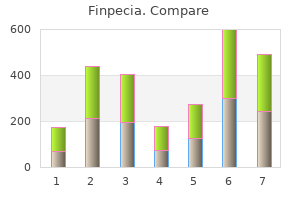
Finpecia
"1 mg finpecia fast delivery, hair loss cure news june 2014".
By: D. Lisk, MD
Co-Director, Columbia University Roy and Diana Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons
Degree of erosion of the ear canal is noted hair loss cure 2013 1mg finpecia for sale, as is involvement of the middle ear or any deeper structures hair loss at 20 discount 1mg finpecia. The parotid gland may be involved by both direct extension and intraparotid nodal metastasis hair loss cure soon discount finpecia 1 mg fast delivery. Arteriography with balloon occlusion may be needed to evaluate suspected intrapetrous carotid artery invasion hair loss treatment yoga cheap generic finpecia uk. An audiogram will be helpful in counseling patients regarding hearing rehabilitation after treatment. There are many different subtypes: well differentiated, moderately differentiated, poorly differentiated, clear cell, spindle cell, and verrucous. N Other Malignant Neoplasms of the Ear and Temporal Bone Melanoma Melanoma of the auricle accounts for almost 1% of all melanomas. Malignant Glandular Tumors Adenoid cystic carcinoma and ceruminous adenocarcinoma present as painful obstructing ear canal masses. Chondrosarcoma Chondrosarcomas occur at the skull base, off midline at the petroclival junction. Chordoma Chordoma is a locally aggressive disease process with a low rate of metastasis. Patients most commonly present with headache or diplopia and usually are 40 to 50 years of age. Sarcoma Sarcoma is the most common malignancy of temporal bone in children, especially rhabdomyosarcoma. There are multiple types, and it usually presents with otitis media, drainage, polyps, and bleeding. Most cases respond to either chemotherapy or radiotherapy, so surgery is limited to diagnostic biopsy with aggressive resection reserved for treatment failures. Metastasis Metastasis is most commonly hematogenous from breast, lung, and kidney. Head and Neck 427 Medical Chemotherapy may have some role in treatment as an adjunct to surgery, usually given postoperatively and in palliative management. There are many common surgical approaches beginning with sleeve resection of the ear canal with some form of mastoidectomy for T1 lesions isolated to the ear canal. Lesions within the canal, but not extending into the middle ear, are approached with a lateral temporal bone resection that removes the ear canal en bloc. Lesions that extend into the middle ear can be resected with subtotal temporal bone resection, which is a lateral temporal bone resection and piecemeal removal of any residual deeper tumor remnants. Total temporal bone resection is reserved for deeply invasive T4 lesions and its utility is controversial. Neck dissection and parotidectomy are often part of the resection; certainly if there is clinically evident nodal spread. N Outcome and Follow-Up Accurate outcomes and survival rates are difficult to find in the literature. T3 and T4 tumors treated with surgery and radiation have 5-year survival rates 50%. Staging proposal for external auditory meatus carcinoma based on preoperative clinical examination and computed tomography findings. The extranodal sites in the head and neck are the thyroid, orbit, salivary glands, and sinonasal passages. A high index of suspicion for lymphoma as a cause of common complaints in the head and neck region can lead to early diagnosis and improved outcome. Beyond the role of diagnostician, the head and neck surgeon will often be the one who obtains tissue for diagnosis.
Maternal blood enters the intervillous spaces of 133 the placenta through about 100 spiral arteries hair loss solutions for women generic finpecia 1 mg otc, baths the villi hair loss cure india purchase finpecia 1mg without a prescription, and leaves again via endometrial veins hair loss 21 buy finpecia 1 mg mastercard. The placenta contains approximately 150ml of maternal blood hair loss medication related buy generic finpecia, and this volume is replaced about three to four times per minute. As the blastocyt implants in the uterine wall, the endometrial stroma thickens to form the decidua. The endometrial glands enlarge, the stromal cells become engorged with lipid and glycogen, and endometrial veins and spiral arteries make connections with the trophoblastic lacunae. Maternal antibodies are able to reach the fetus via the placenta, and in this way, gives the fetus some immunity against a variety of infections. This limited immunity persists in the newborn for several months, allowing it to fight off infections until its own immune system develops. One complication that can develop as a result of antibodies being transferred from the mother to the fetus is Erythroblastosis fetalis. In this condition antibodies are directed against an Rh factor on the surface of fetal red blood cells and cause hemolysis of the fetal red blood cells. Aside from providing the fetus with nutrients and antibodies, the placenta produces the steroid hormones, progesterone and estrogen, which are responsible for maintaining the state of pregnancy and preventing spontaneous abortions or preterm labor. In addition, the placenta produces prostaglandins, which is involved in the maintenance of pregnancy and onset of labor. Although the reduced ratio of progesterone to estrogen, during the ninth month, is thought to initiate labor it appears that this may be mediated by prostaglandin levels produced by the placenta. In amniocentesis, amniotic fluid, which contains metabolic byproducts of the fetus as well as sloughed cells, is removed from the amniotic cavity and examined for various clues to fetal disease. The presence of the protein alpha-fetoprotein in the amniotic sample suggests the presence of an open neural tube defect such as anencephaly. In chorionic sampling, a catheter is used to remove a small sample of chorionic tissue, which can be karyotyped for evidence of fetal genetic diseases. In ultrasonography, the inside of the body is scanned by an ultrasonic beam, which creates a pattern of echoes that are returned to a computer and analyzed (fig. A needle is inserted through the lower abdominal wall and uterine wall into the amniotic cavity. This technique is usually performed at about the ninth week after the last menstrual period. Two sampling approaches are illustrated: through the maternal anterior abdominal wall with a spinal needle, and through the vagina and cervical canal using a malleable cannula. The smaller circular structure (long arrows) is the fetal skull; the large, thinwalled, cushion-like structure posterior to it (short arrows) is a cystic hygroma in the cervical region. Eventually, the cervix will reach 100% effacement and be completely thinned out (3). The opening will continue to enlarge (5) until it reaches a diameter of ten centimeters, at which time the baby can pass through. When the uterus contracts during labor, it puts pressure on the baby to move it downward through the pelvis and vagina. These contractions also serve to dilate the cervix, which is the portion of the uterus that protrudes into the vagina (fig. However, before 137 the cervix can dilate enough to allow for passage of the baby, it must soften and thin out, which is called effacement. If, for example, the cervix has thinned out to half its normal size it is called 50% effaced; if completed thinned out it is 100% effaced. During labor, the cervix continues to efface, while the opening of the cervix starts to dilate. Eventually, when the opening of the cervix has reached 10 centimeter, the cervix is termed fully dilated and the baby can be pushed from the uterus. In approximately 97% of pregnancies, the baby is in a head-first or cephalic position (fig. Other Figure 8: In most pregnancies, the baby presents in a cephalic position, with his head nearest to the cervix. In a small percentage of pregnancies, the baby presents in a breech position, with his buttocks or feet nearest the cervix.
Ask about smoking hair loss postpartum proven 1mg finpecia, tobacco chewing hair loss kittens generic 1mg finpecia visa, alcohol use hair loss cure future generic finpecia 1mg amex, fever hereditary hair loss cure order finpecia 1mg overnight delivery, pain, weight loss, night sweats, exposure to tuberculosis, animals, pets, and occupational/sexual history. Physical Exam All mucosal surfaces of the nasopharynx, oropharynx, larynx, and nasal cavity should be visualized by direct examination or by indirect mirror or fiberoptic visualization. Regarding the neck mass, emphasis on location, tenderness, mobility, and consistency of the neck mass can often place the mass within a general etiologic grouping. Criteria such as heterogeneity of the center of the mass, blurred borders, and a round shape are suggestive of malignancy. Contrast should be used except in the suspected thyroid lesion as it may interfere with radioactive-iodine imaging studies or therapy. Ultrasound is helpful in differentiating solid from cystic masses and congenital cysts from solid lymph nodes and glandular tumors. More specialized laboratory tests may become necessary as the investigation proceeds. Panendoscopy: If careful examination in the office does not identify the etiology of the neck mass and a tumor is suspected, the upper aerodigestive tract should be examined under anesthesia. G N Treatment Options Medical A tender, mobile mass or one highly suggestive of inflammatory or infectious etiology may warrant a short clinical trial of antibiotics and observation with close follow-up. Use steroids judiciously; steroids may shrink a neck mass caused by lymphoma lulling the physician and patient into a false sense that the condition is improving. Surgical G G G G Open excisional biopsies should be avoided in cases in which a nonlymphoma malignancy (epidermoid, melanoma) is suspected. The patient and surgeon should be prepared to proceed immediately with a complete neck dissection depending on the results of frozen sections. Inflamed congenital masses are typically treated with antibiotics and then surgically removed after inflammation has subsided. Surgery in the form of incision and drainage is used in cases that do not respond to appropriate medical therapy. Squamous cell carcinoma metastatic to the neck from an unknown head and neck primary site. There is a propensity for second primary tumors (between 4 and 7% per year), especially if still smoking. Specific sites and subsites of head and neck cancer are discussed in subsequent chapters. These cancers are more common in men, and typically occur in patients over age 50. The etiology includes tobacco use (smoking and smokeless) and alcohol consumption. The synergistic effect of alcohol and smoking increases the risk of disease many more times than the simple additive risk of either risk factor alone. Head and Neck 347 N Clinical Signs Signs may include hoarseness, muffled speech, trismus, and recurrent epistaxis. Many patients present with a neck mass as chief complaint, representing metastatic nodal disease from an occult primary tumor in the upper aerodigestive tract (Table 5. Early symptoms may be vague and mimic benign disease and are therefore only discovered at advanced stages of disease. Differential Diagnosis G Upper respiratory infections such as pharyngitis, laryngitis, deep neck infections or abscesses Congenital masses and cysts Upper airway manifestations of rheumatologic and autoimmune diseases Hematologic malignancies (lymphoma) Tuberculosis Fungal infections G G G G G Table 5. Physical Exam Physical exam should include careful inspection of the oral and oropharyngeal mucosa for lesions, and palpation of the tonsillar region and tongue base for firm nodules or masses. During this examination, the patient should be asked to perform several maneuvers such as tongue protrusion, puffing out the cheeks, lightly coughing and speaking to better visualize and access the larynx and the hypopharynx. It is important that laryngeal motility be assessed, as this is critical in tumor staging. Any palpable lymph nodes should be assessed with regard to size, location, and mobility.
Order finpecia 1 mg fast delivery. Real Questions - Can you stimulate facial hair growth?.
Principles of surgical treatment Surgical treatment is now reserved for those patients in whom complications of ulceration occur hair loss cure prostaglandin d2 discount finpecia 1mg with mastercard. In the emergency situation hair loss in men quote discount finpecia express, minimal surgery is practised with the confidence that medical cure of the underlying disease may be effected hair loss in men quilters purchase finpecia once a day. The commonest indications for emergency surgery are bleeding or perforation (see below) hair loss joint pain purchase finpecia 1 mg without prescription. This can be effected by removing the bulk of the acid-secreting area of the stomach (the body and the lesser curve), and re-establishing gastric drainage via a Roux-en-Y Treatment Treatment of a peptic ulcer is medical in the first instance; surgery is indicated when complications supervene. The complications are chronicity, perforation, stenosis, haemorrhage and, in the case of gastric ulcer, malignant change. Principles of medical treatment the main principles of treatment are to eradicate H. He performed the first successful gastrectomy for cancer at the pyloric end of the stomach in 1881. Surgery is still indicated in the presence of haemorrhage from an ulcer, and usually comprises a partial gastrectomy with drainage into a Roux-en-Y loop of jejunum. As total vagotomy interferes with the mechanism of gastric emptying, this operation must be accompanied by a drainage procedure, either gastrojejunostomy or pyloroplasty. If the branches of the vagus that supply the pyloric sphincter (the nerves of Latarjet9) are left intact, the remaining vagal fibres can be divided without the necessity of gastric drainage (highly selective vagotomy), but nevertheless the goal of reduction in the vagal phase of acid secretion is achieved. This is probably an osmotic effect due to gastric contents of high osmolarity passing rapidly into the jejunum, absorbing fluid into the gut lumen and producing a temporary reduction in circulating blood volume. In the presence of a long afferent loop, food passing into the jejunum traverses the bowel without mixing adequately with pancreatic and biliary secretions. A stomal ulcer, like any other peptic ulcer, may perforate, stenose, invade surrounding structures or bleed. Frequently transient or episodic, they may be severe and persistent in about 2% of patients. The incidence is reduced in patients subjected to highly selective vagotomy without drainage. Both gastric ulcer and gastric carcinoma are common conditions and there may merely be a chance association between the two. Perforated peptic ulcer Pathology Perforation of a peptic ulcer is a relatively common and important emergency. Treatment A nasogastric tube is passed to empty the stomach and diminish further leakage. Opiate analgesia is given to relieve pain and an intravenous fluid resuscitation is started. Antibiotics are given to contend with the peritoneal infection, and an intravenous H2-blocker or proton pump inhibitor commenced. Surgery involves suturing an omental plug to seal the perforation, together with lavage of the peritoneal cavity.
In Mediterranean hair loss on arms generic finpecia 1 mg fast delivery, Middle Eastern and Oriental popula tions hair loss in men kids buy finpecia 1 mg amex,affectedmaleshaveveryloworabsentenzyme activityintheirredcells hair loss 3 months after stress buy generic finpecia on line. This is associated with fever hair loss 11 year old cheap finpecia 1mg without a prescription, malaise and the passage of dark urine, as it contains haemo globin as well as urobilinogen. Diagnosis Between episodes, almost all patients have a com pletely normal blood picture and no jaundice or anaemia. Management Theparentsshouldbegivenadviceaboutthesignsof acutehaemolysis(jaundice,palloranddarkurine)and provided with a list of drugs, chemicals and food to avoid(Box22. Clinical manifestations Childrenusuallypresentclinicallywith: Haemoglobinopathies Theseareredbloodcelldisorderswhichcausehaemo lyticanaemiabecauseofreducedorabsentproduction ofHbA(andthalassaemias)orbecauseofthepro duction of an abnormal Hb. Worldwideitisthemostcommon causeofsevereneonataljaundicerequiring exchangetransfusion 1 2 3 Haematological disorders 387 4 Table 22. Haematological disorders Pathogenesis In all forms of sickle cell disease, HbS polymerises within red blood cells forming rigid tubular spiral bodieswhichdeformtheredcellsintoasickleshape. Irreversibly sickled red cells have a reduced lifespan andmaybetrappedinthemicrocirculation,resulting in blood vessel occlusion (vasoocclusion) and there foreischaemiainanorganorbone. Clinical manifestations of the haemo globinopathiesaffectingthechainaredelayeduntil after 6 months of age when most of the HbF present at birth has been replaced by adult HbA. Streptococcus pneumoniaeandHaemophilus influenzae typeBbecauseoffunctionalasplenia,childrenshould be fully immunised, including against pneumococcal, Haemophilus influenzae type B and meningococcus infection. Toensurefullcoverageofallpneumococcal subgroups, daily oral penicillin throughout childhood should be given. Vaso occlusivecrisesshouldbeminimisedbyavoidingexpo sure to cold, dehydration, excessive exercise, undue stressorhypoxia. Thisrequirespracticalmeasuressuch as dressing children warmly, giving drinks especially beforeexerciseandtakingextracaretokeepchildren warmafterswimmingorwhenplayingoutsideinthe winter. Sickle cell disease is the collective name given to haemoglobinopathies in whichHbSisinherited. Sickle cell diseaseis most common in patients whose parents are black and originate from tropical AfricaortheCaribbeanbutitisalsofoundintheMiddle Eastandinlowprevalenceinmostotherpartsofthe worldexceptfornorthernEuropeans. There is also an increased incidence of osteomyelitis caused by Salmonella and other organisms. This susceptibility to infection is due to hyposplenism secondary to chronic sickling and microinfarction in the spleen in infancy. The risk of overwhelming sepsis is greatest in early childhood Vaso-occlusive crises causing pain affect many organs of the body with varying frequency and severity. A common mode of presentation in late infancy is the hand-foot syndrome, in which there is dactylitis with swelling and pain of the fingers and/or feet from vaso-occlusion. The most serious type of painful crisis is actute chest syndrome, which can lead to severe hypoxia and the need for mechanical ventilation and emergency transfusion. Herbreath ing was laboured, respiratory rate increased and therewasreducedairentryatbothbases. A diagnosis of acute sickle chest syndrome was made, a potentially fatal condition. Prognosis Sicklecelldiseaseisacauseofprematuredeathdueto one or more of these severe complications; around 50%ofpatientswiththemostsevereformofsicklecell disease die before the age of 40 years. However, the mortality rate during childhood is around 3%, usually frombacterialinfection. Early diagnosis of sickle cell disease allows penicillin prophylaxis to be started in early infancy instead of awaiting clinical presentation, pos siblyduetoasevereinfection.