Mebendazole
"Order on line mebendazole, antiviral body wash".
By: P. Wenzel, M.B.A., M.D.
Clinical Director, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine
The initiation and completion of adolescence are highly variable among individuals hiv symptoms eye infection safe 100 mg mebendazole. Humans have a prolonged adolescent development in which the conclusion is not defined by physiologic milestones antiviral for shingles purchase mebendazole 100mg with amex, but by less clear-cut sociologic parameters that may vary widely among different societies hiv infection in korea purchase 100 mg mebendazole with amex. During this phase hiv-1 infection cycle mebendazole 100 mg otc, the adolescent must discover who he or she is and develop a unique identity, separate from family and other adults. According to this theory, the attainment of a realistic self-identity is a milestone for the passage into adulthood. Stages of Adolescence the psychosocial development of the adolescent can be divided into three distinct phases: early, middle, and late adolescence. During early adolescence, childhood roles are cast aside and dependent emotional ties with the family severed. The first signs of independence may occur when the adolescent becomes less involved and less interested in long-standing family activities and routines. It is common at this stage for the adolescent to bristle and become resistant when criticized or when given unsolicited advice by adults or authority figures. Within a short period, the once-obedient child may become rebel391 B efore reaching adulthood, every person passes through the stages of infancy, childhood, and adolescence. During adolescence, much time is spent developing the skills and talents that will guide individual career and vocational plans. Once the adolescent develops a stable self-identity with which he or she is confident, mature intimate relationships with other adults can be entered into without the fear of losing self-identity. At times, the adolescent may be fearful of relinquishing the security of childhood and when stressed may revert to childlike behavior. To ease the transition into the early phase of adolescence, parents and other adults must recognize this assertion of independence as a part of normal development and when possible allow the teenager some degree of freedom of choice. During the middle phase of adolescence, the teenager begins to seek a new identity through peer group involvement. New emotional ties with the peer group fill the psychological void left by the abandonment of childhood dependence on parents. Participation in peer group activities reinforces the sense of separation from parents and facilitates emotional separation from them. Adolescent groups may adopt outlandish clothes or styles to clearly differentiate themselves from their parents and other adults. Paradoxically, peer groups discourage individuality and the development of self-identity-the adolescent must either conform to the ways of the peer group, or cease to be a member. At this stage, however, adolescents are not seeking a distinct identity but rather a stable one. Interpersonal relationships in the peer group are often superficial, and individual identity is highly compromised by pressures to conform to group standards. At the conclusion of middle adolescence, peer groups dissolve as individuality and self-identity increase. An adolescent with no friends, or poor peer group ties, may experience problems in facilitating the development of self-identity and independence. In late adolescence, physical ties with the family are severed as the adolescent moves out of the home, becomes financially more self-sufficient, and accepts adult roles and responsibilities. With the eventual attainment of a stable self-identity and independence, the young adult accepts mature relationships with other adults without experiencing fear of losing control of his or her selfidentity. Problems in these relationships may occur when an individual seeks to maintain peer group ties and/or family dependence. Although these stages describe adolescent development in most North American and European families, considerable variation in the sequence may exist in other areas of the world. In many cultures, extended multigenerational families living together are the cultural norm. In some cultures, the passage into adulthood is clearly defined by a ritual passage or event. Once the adolescent has demonstrated completion of the rite of passage, acceptance as an adult member of the society occurs. Between 2010 and 2025, the total number of 13- to 18year-olds has been projected to show a modest increase, although decreasing slightly as a percentage of the total population. As a result, the size of the adolescent population will remain relatively stable, but as more people live longer, the proportion of the total population who are adolescents will decrease.
Identify any cultural or linguistic differences and any behavioral factors that may be contributing to the breakdown in functional communication hiv infection rate kenya order mebendazole cheap online. Assessment of the oral mechanism Muscle function of the jaw hiv symptoms first year infection effective mebendazole 100mg, lips and tongue and the integrity of the oral structures (hard and soft palate hiv infection in toddlers buy mebendazole once a day, jaw hiv infection cdc cheap 100mg mebendazole fast delivery, lips and tongue). Reading (nonreaders may be substituted with structured verbal tasks such as picture or object description). Analysis of accessory behaviors (verbal interjections, eyebrow raising, eye blinking, rolling, closure, head/jaw jerking and/or hand/arm movement). Inventory of stuttering events (core behaviors: sound/syllable repetition, wholeword repetition, phrase or sentence repetition, sound prolongation, inaudible prolongations or blocks). Video recording to capture and document verbal and nonverbal components of a fluency disorder. Interpret the clinical findings of the fluency disorder evaluation that will include: A clinical diagnosis of fluency disorder based upon a combination of characteristics identified during the assessment process. Cluttering may be combined with stuttering and contribute to slower progress and less favorable outcomes due to the underlying language issues and general poor awareness of speech errors. Determine the needs and abilities of the individual, family concerns, parental concerns, impact of stuttering on emotional health and functional ability to communicate ideas across all environments. Determine potential for attitudinal, compensatory and functional improvement within a reasonable time frame. Develop an individual program designed to address symptoms and secondary characteristics of stuttering. Develop a treatment plan that emphasizes implementation of strategies in a variety of communication situations within his/her home, school and/or community. Provide family members, caregivers, guardian, siblings, school teachers and/or other communication partners training in communication techniques and strategies to facilitate effective communication. Provide individuals and parents with information regarding community support groups and/or programs. Cluttering symptoms are best treated using kinesthetic and proprioceptive techniques. Select and implement appropriate equipment and computer software to communicate effectively and efficiently in a variety of communication situations within his/her home, school and/or community. Treatment intensity is variable and may include intense outpatient or inpatient residential programs. Provide suggestions and resources for follow-up Provide home program to continue to progress and/or to maintain gains If discharged due to medical issues and/or plateau in progress, indicate under what future conditions a new referral would be warranted. Show measurable progress toward goals and reason not attained such as: fluctuations in abilities and/or motivation. Show evidence that education was provided and response to it Include attainment, updates or changes in short or long-term goals and/or changes in intensity or type of treatment. Referral to local support groups both during treatment and after treatment for long term practice and support. Treatment Plan Timeline Frequency and duration of services is based upon specific needs of the individual at the time of the evaluation. Individuals with fluency disorder tend to have periods where they plateau then will go on to make functional improvements. Lidcombe program webcam treatment for early stuttering: A randomized controlled trial. Management options for pediatric patients who stutter: Current challenges and future directions. The relationship between grammatical development and disfluencies in preschool children who stutter and those who recover. The neurobiological grounding of persistent stuttering: From structure to function. Proton chemical shift imaging of the brain in pediatric and adult developmental stuttering. Evidence for the treatment of co-occurring stuttering and speech sound disorder: A clinical series. A lag in speech motor coordination during sentence production is associated with stuttering persistence in young children.
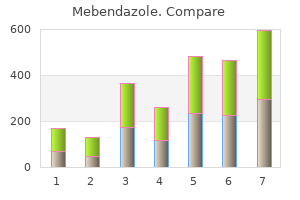
Buy mebendazole american express. AIDS sufferers in Russia | Global 3000.
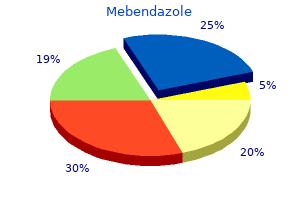
Syndromes
- Pheochromocytoma
- Oxygen
- Yellow skin and eyes (jaundice)
- High blood pressure
- Racing heart
- Rapid breathing
- Ask your doctor which drugs you should still take on the day of your surgery.
- Confirm the person has ADHD