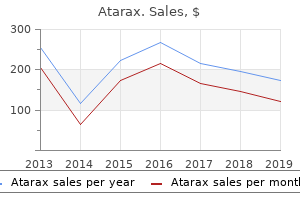
Atarax
"Cheap atarax 10 mg without prescription, anxiety symptoms 7 year old".
By: M. Jens, M.B. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, University of Nevada, Las Vegas School of Medicine
Leg cramps are experienced by almost half of all pregnant women anxiety or adhd order atarax 25mg mastercard, particularly at night and in the later months of pregnancy anxiety or ms buy generic atarax online. Bothcalcium andsodiumchloridesupplementationappeartohelp reduce leg cramps in pregnancy anxiety lexapro generic atarax 25mg on-line. Recently anxiety 3 months postpartum purchase generic atarax, vitamin D deficiency in both men and women has been associatedwithlegcrampsandmusclepain. Backaches are common during pregnancyandare lessened by avoiding excessive weight gain. Additionally, exercise, sensible shoes, and specially shaped pillows can offer relief. In cases of muscle spasm or strain, analgesics (such as acetaminophen), rest, and heatmaylessenthesymptoms. Maternal obesity may occur over time between pregnancies because of the difficulty that some women have returning to prepregnancy body weight. Althoughweightgainisanimportantconsideration duringpregnancy,the clinician should emphasize the "right amount of nutrition" over the "right amount of weight gain. Advice regarding work shouldbeindividualizedtothenatureofthework,the health status of the woman, and the condition of the pregnancy. Work that requires prolonged standing, shiftornightwork,andhighcumulativeoccupational fatiguehasbeenassociatedwithanincreasedriskfor lowbirthweightandprematurity. Where working conditions involve occupational fatigue or stress, a change in work conditions during pregnancy should be recommended. Any type of exercise involving the potential for loss of balance or even mild abdominal trauma should be avoided. Pregnant women should beencouragedtoambulateperiodicallywhentakinga long flight or car ride. International travel that places the patient at a high risk of exposure to infectious disease should be avoided, whenever possible. Increased, unchanged, and decreased levels of sexual activity can all be normal during pregnancy. Abstinenceorcondomusemaybeadvisableifthereis an increased risk of preterm labor or repeated pregnancy loss, or in women with a history of persistent second-orthird-trimesterbleeding. Thescheduleof these follow-up visits, however, should be tailored to the needs of individual patients. Women should be screened for depression early in pregnancy, during the third trimester and again postpartum. The incidence of depression during pregnancy and the postpartum period is as high as 20%. Multiple studies have shown a significant relationship between vitamin D deficiency and depression. Duringeachregularlyscheduledvisit,theclinician shouldevaluatebloodpressure,weight,urineprotein and glucose, uterine size for progressive growth, and fetal heart rate. Between 24 and 34 weeks, women should be taught the warning symptoms of preterm labor (uterine contractions, leakageoffluid,vaginalbleeding,lowpelvicpressure, or low back pain). Patients at risk may require additional visits to assess signs and symptoms of preterm labor. Beginning in the late second trimester, they shouldalsobetaughttorecognizethewarningsymptomsofpreeclampsia(frontalheadache,visualchanges, handorfacialswelling,epigastricorrightupperquadrantpain). Beginning at 28 weeks, systematic examination of the abdomen should be carried out at each prenatal visit to identify the lie. Thefirst maneuverinvolves palpating the fundus to determine which part of the fetusoccupiesthefundus. The second maneuver involves palpating either side of the abdomen to determine on which side the fetal back lies. The third maneuver involves grasping the presenting part between the thumbandthirdfingerjustabovethepubicsymphysis todeterminethepresentingpart. Thefourth maneuverinvolvespalpatingforthebrowandtheocciputof the fetus to determine fetal head position when the fetus is in a vertex presentation. Providers should initiate discussion with the pregnant woman and her family regardingbreastfeedingduringthefirstvisit,including possible barriers to breastfeeding, such as previous poor experiences, misinformation, or nonsupportive work environment. Clinicians should emphasize that weightgainduringpregnancyistosupportfetalgrowth andfordevelopmentofanutritionalreservetosupport effective breastfeeding. Breastfeeding for at least 6 months will facilitate complete loss of the required weight gain during pregnancy.
Diseases
- Giant cell arteritis
- Cryptococcosis
- Reginato Shiapachasse syndrome
- Ohaha syndrome
- Nonsyndromic hereditary hearing impairment
- Lipomatosis familial benign cervical
- Sialidosis
At the levels recommended in the guidelines for the use of the various fluoride modalities anxiety attack symptoms quiz atarax 10 mg discount, no adverse health effect is considered likely anxiety disorders discount atarax 25mg on line. Fluoride acts for the most part anxiety questionnaire pdf discount atarax 10mg otc, topically can anxiety symptoms kill you buy discount atarax 25 mg line, promoting remineralization and reducing demineralization as a post-eruptive phenomenon. Fluoride can prevent mineral loss at crystal surfaces and enhance remineralization with calcium and phosphate ions. Because the mode of action of fluoride is predominantly post-eruptive, the prevention of caries requires lifelong exposure. When remineralization takes place in the presence of fluoride the remineralized enamel is more caries resistant than the original enamel mineral due to increased fluoroapatite and decreased carbonated apatite. Fluoride has an effect on the glycolytic pathway of oral micro-organisms reducing acid production and interfering with the enzymatic regulation of carbohydrate metabolism. This reduces the accumulation of intracellular and extracellular polysaccharides. The continuous presence of low levels of fluoride at the plaque fluidenamel interface provides the most effective mode of remineralization of demineralized enamel. This topical effect explains the efficacy of fluoridated toothpastes, gels, fluoride rinses and fluoride in drinking water. With concentrated topical fluoride application such as from fluoride varnishes and gels, the formation of calcium fluoride is favoured, persisting in the pores of enamel for extended periods and acting as a fluoride reservoir during remineralization. Community water fluoridation the naturally occurring concentration of fluoride in drinking water in Australia is typically in the range of 0. Fluoride is added to reticulated community water supplies of most large urban populations to achieve a concentration of between 0. Fluoride Modalities 55 Caries reduction the caries reduction of 2040% now recorded in fluoridated communities is considerably less than was the case when water fluoridation was first introduced into contemporary Western populations because of the general increase in availability of fluoride from other sources. There is a reversal of protective benefits after removal of fluoride from water supply. There is a decreased prevalence of root-surface caries in lifelong inhabitants of areas with fluoridated water. Considering the cost effectiveness and widespread community exposure, the preferred source of fluoride is from community water fluoridation. In Western communities, the continuing existence of approximately 20% of children with a high caries experience indicates the need to maximize protection through the combined use of community water fluoridation and topical fluoride modalities. Bottled and filtered waters Bottled waters have shown rapid market growth, and for many individuals water consumption from this source may have fully replaced use of reticulated water. Since the fluoride content of bottled water may be very low (unless supplemented during manufacture), consumers of bottled water in fluoridated communities may be missing out on the benefits of fluoride. Some water filters may remove fluoride, although this is mostly limited to those filters with reverse osmosis, bone or charcoal filters, distillation or ion exchange. Individuals should have choice in bottled and filtered waters, and manufacturers are encouraged to market bottled waters of 1. Bottled waters and water filters should be labelled to indicate the fluoride content of water consumed or resulting from the use of such products. The fluoride tablets previously marketed as oral supplements may now be used as water supplements as follows to supplement filtered water to the level of 1 ppm F-: One 2. The fluoridated water should then be refrigerated and used for drinking and food preparation for the entire family. Home water fluoridation Approximately 70% of the Australian population benefits from fluoridation of reticulated water. In areas that are non-fluoridated, there should be a choice of home 56 Handbook of Pediatric Dentistry fluoridation. It has been recommended that sodium fluoride tablets should be marketed as a water supplement for addition to non-fluoridated water to achieve 1 mg F-/L (1 ppm F-). Dental fluorosis (see Chapter 9) Dental fluorosis is a qualitative defect of enamel (hypomineralization), resulting from an increase in fluoride concentration within the microenvironment of the ameloblasts during enamel formation. In more severe forms, fluorosis may also manifest as a quantitative defect (hypoplasia). This trend has been apparent in both fluoridated (a 33% increase) and non-fluoridated communities and is caused by the additive effects of the following: Fluoride supplements (as tablets or drops).
Purchase atarax with a visa. Anxiety - My Mental Health Story.
In addition to their genetic differences from bacteria anxiety symptoms rash atarax 10mg lowest price, archaeans have some chemical differences anxiety symptoms 100 cheap atarax 10 mg line, including the fact that their cell walls are never made of peptidoglycan anxiety yahoo order genuine atarax on-line. This domain contains familiar organisms such as animals anxiety disorders symptoms quiz purchase atarax amex, plants, mushrooms, and seaweed. Hence the creation of the taxonomic hierarchy, a naming system that ranks organisms by their evolutionary relationships. Within this hierarchy, living things are organized into the largest, most-inclusive group down to the smallest, least-inclusive group. Whatever characteristics are used to define a category must be shared by all organisms placed into that category. For example, organisms in domain Eukarya are separated from those in the Bacteria and Archaea domains based on whether their cells have a nucleus, the types of molecules found in the cell wall and membrane, and how they go about protein synthesis. Kingdom: Kingdoms group organisms based on developmental characteristics and nutritional strategy. For example, organisms in the animal kingdom (Animalia) are separated from those in the plant kingdom (Plantae) because of differences in the early development of these organisms and the fact that plants make their own food by photosynthesis whereas animals ingest their food. For example, within kingdom Plantae, flowering plants (Angiophyta) are in a different phylum than cone-bearing plants (Coniferophyta). Class: Classes separate organisms based on key characteristics that define the major groups within the phylum. For example, within phylum Angiophyta, plants that have two seed leaves (dicots, class Magnoliopsida) are in a separate class than plants with one seed leaf (monocots, class Liliopsida). Order: Orders separate organisms based on key characteristics that define the major groups within the class. For example, within class Chapter 10: Biodiversity and Classification Magnoliopsida, nutmeg plants (Magnoliales) are put in a different order than black pepper plants (Piperales) due to differences in their flower and pollen structure. Family: Families separate organisms based on key characteristics that define the major groups within the order. For example, within order Magnoliales, buttercups (Ranunculaceae) are in a different family than roses (Rosaceae) due to differences in their flower structure. Genus: Genera separate organisms based on key characteristics that define the major groups within the family. For example, within family Rosaceae, roses (Rosa) are in a different genus than cherries (Prunus) thanks to differences in their flower structure. Species: Species separate eukaryotic organisms based on whether they can successfully reproduce with each other. You can walk through a rose garden and see many different colors of China roses (Rosa chinensis) that are all considered one species because they can reproduce with each other. Think of how biologists organize living things like how you might organize your clothing. In your first round of organizing, you might make groups of pants, shirts, socks, and shoes. From there, you might go into the shirt group and organize your shirts into smaller groups, such as short-sleeved versus long-sleeved shirts. All of your clothing would be organized in a hierarchy, from the big category of clothing all the way down to the small category of short-sleeved, button-down, blue shirts. The first letter of each word in the sentence represents the first letter of a category in the taxonomic hierarchy. All life on Earth is related, but relative position within the taxonomic hierarchy demonstrates the degree of that relationship. For instance, you and a carrot are both in domain Eukarya, so you definitely have some things in common, but you have more characteristics in common with organisms that are part of the animal kingdom. Table 10-1 compares the classification, or taxonomy, of you, a dog, a carrot, and E. However, you also have many differences, including the tooth structure that separates you into the order Primates and a dog into the order Carnivora. If you compare yourself to a plant, you can see that you have certain features of cell structure that place you together in domain Eukarya, but little else in common. For most eukaryotic organisms, members of the same species can successfully sexually reproduce together, producing live offspring that can also reproduce.
African Wild Potato. Atarax.
- Dosing considerations for African Wild Potato.
- What other names is African Wild Potato known by?
- Lung cancer, bladder infections, cancer, lung disease, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), tuberculosis (TB), arthritis, a skin condition called psoriasis, wound healing, and improving the immune system.
- Trouble urinating because of an enlarged prostate, or "benign prostatic hyperplasia" (BPH).
- How does African Wild Potato work?
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96661