Atacand
"Buy genuine atacand, hiv infection rate in singapore".
By: K. Rathgar, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Associate Professor, Florida State University College of Medicine
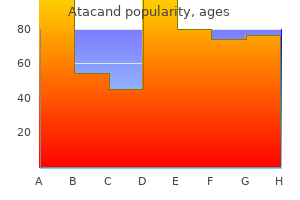
A new drug was administered to a group of normal volunteers in a phase 1 clinical trial hiv infection rate in us atacand 16mg on line. Intravenous bolus doses produced the changes in blood pressure and heart rate shown in the graph below quantum antiviral formula discount 16mg atacand with visa. An example of a phase I drug-metabolizing reaction is (A) Acetylation (B) Glucuronidation (C) Hydroxylation (D) Methylation (E) Sulfation Questions 13 and 14 highest infection rates of hiv/aids cheap 16mg atacand with amex. A 52-year-old plumber comes to the office with a complaint of periodic onset of chest pain hiv infection rates worldwide generic 8mg atacand visa, described as a sensation of heavy pressure over the sternum that comes on when he exercises and disappears within 15 min when he stops. After a full physical examination and further evaluation, you make the diagnosis of angina of effort. In considering medical therapy for this patient, which of the following best describes the beneficial action of nitroglycerin in this condition A drug that is useful in angina but causes constipation, edema, and increased cardiac size is (A) Atenolol (B) Hydralazine (C) Isosorbide dinitrate (D) Nitroglycerin (E) Verapamil 15. A 15-year-old girl is admitted complaining of palpitations and shortness of breath. A drug suitable for producing a brief (5- to 15-min) increase in cardiac vagal effects is (A) Digoxin (B) Edrophonium (C) Ergotamine (D) Pralidoxime (E) Pyridostigmine 16. A patient with a 30-yr history of type 1 diabetes comes to you with a complaint of bloating and sour belching after meals. Evaluation reveals delayed emptying of the stomach, and you diagnose diabetic gastroparesis. Persons who ingest three or more alcoholic drinks daily can develop severe hepatotoxicity after doses of acetaminophen that are not toxic to individuals with normal liver function. A 70-year-old woman with mild to moderate hypertension fell 2 yr ago during a spell of dizziness and broke her hip. A 52-year-old woman is admitted to the emergency department with a history of drug treatment for several conditions. A 54-year-old farmer has a 5-yr history of frequent, recurrent, and very painful calcium-containing kidney stones. The patient has hypercalciuria caused by a primary defect in proximal tubule calcium reabsorption. A 56-year-old woman has arthritis of the knees that limits her activity and post-herpetic neuralgia on her torso after an episode of herpes zoster. Which of the following drugs is used topically to control arthritic pain and post-herpetic neuralgia In your pursuit of a Nobel Prize, you have been studying several intracellular enzymes. The number of episodes of severe bronchospasm has increased recently, and you have been asked to review the therapeutic plan. Which of the following agents is most likely to be of immediate therapeutic value in relieving an acute bronchospastic attack When she went on vacation and forgot her pills, her blood pressure rose markedly and she was admitted to the emergency service with blurred vision, severe headache, and retinal hemorrhages. A drug that is most likely to be followed by severe rebound hypertension if stopped suddenly is (A) Atenolol (B) Clonidine (C) Labetalol (D) Losartan (E) Prazosin 21. Ventricular muscle from a cardiac biopsy was prepared for transmembrane potential recording in an isolated muscle chamber. A long-acting 2-selective agonist that is used as an inhaled prophylactic therapy for moderate or severe asthma is (A) Ipratropium (B) Montelukast (C) Salmeterol (D) Theophylline (E) Zafirlukast 29. If a patient mistakenly receives a toxic dose of lidocaine intravenously, the patient is likely to exhibit (A) Cardiovascular stimulation (B) Excessive salivation, mydriasis, and diarrhea (C) Hyperthermia and hypertension (D) No effects immediately but then delayed, massive hepatocellular damage (E) Seizures and coma 30. Early in an anesthesia procedure, which includes the use of succinylcholine and halothane, a surgical patient develops severe muscle rigidity, hypertension, and hyperthermia. Management of this patient will almost certainly include the administration of (A) Baclofen (B) Dantrolene (C) Fentanyl (D) Naloxone (E) Tubocurarine 31. Which of the following is an inhibitor of fungal cell membrane synthesis and is effective intravenously in the management of disseminated infections due to Aspergillus or Candida species A 5-year-old boy was diagnosed as having an intestinal infection with Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm).
Termination of exposure (decontamination) by removing the patient to fresh air (for inhaled poisons) hiv infection rate ukraine generic atacand 16 mg with mastercard, washing the skin and eyes (for poisons entering from the surface) acute hiv infection symptoms duration purchase discount atacand online, induction of emesis with syrup ipecac or gastric lavage (for ingested poisons) antiviral breastfeeding cheap 4mg atacand with amex. Emesis should not be attempted in comatose or haemodynamically unstable patient hiv infection parties best buy for atacand, as well as for kerosene poisoning due to risk of aspiration into lungs. Emesis/gastric lavage is not recommended if the patient presents > 2 hours after ingesting the poison; if the poison/its dose ingested are known to be non life-threatening, or if the patient has vomited after consuming the poison. However, strong acids and alkalies, metallic salts, iodine, cyanide, caustics, alcohol, hydrocarbons and other organic solvents are not adsorbed by charcoal. Charcoal should not be administered if there is paralytic ileus or intestinal obstruction or when the patient reports > 2 hours after ingesting the poison. However, excretion of many poisons is not enhanced by forced diuresis and this procedure is generally not employed now. It is the converse of tolerance and indicates a low threshold of the individual to the action of a drug. The drug interacts with some unique feature of the individual, not found in majority of subjects, and produces the uncharacteristic reaction. As such, the type of reaction is restricted to individuals with a particular genotype (see p. In addition, certain bizarre drug effects due to peculiarities of an individual (for which no definite genotype has been described) are included among idiosyncratic reactions. The target organs primarily affected in drug allergy are skin, airways, blood vessels, blood and gastrointestinal tract. One drug can produce different types of allergic reactions in different individuals, while widely different drugs can produce the same reaction. The course of drug allergy is variable; an individual previously sensitive to a drug may subsequently tolerate it without a reaction and vice versa. Anaphylaxis is usually heralded by paresthesia, flushing, swelling of lips, generalized itching, wheezing, palpitation followed by syncope. Manifestations are rashes, serum sickness (fever, arthralgia, lymphadenopathy), polyarteritis nodosa, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (erythema multiforme, arthritis, nephritis, myocarditis, mental symptoms). Humoral Type-I (anaphylactic) reactions Reaginic antibodies (IgE) are produced which get fixed to the mast cells. It acts slowly, but is specially valuable for prolonged reactions and in asthmatics. Skin tests (intradermal, patch) or intranasal tests may forewarn in case of Type I hypersensitivity, but not in case of other types. Drugs involved in acute phototoxic reactions are tetracyclines (especially demeclocycline) and tar products. Drugs causing chronic and low grade sensitization are nalidixic acid, fluoroquinolones, dapsone, sulfonamides, phenothiazines, thiazides, amiodarone. Rarely antibodies mediate photoallergy and the reaction takes the form of immediate flare, itching and wheal on exposure to sun. Even small doses may trigger the reaction and lesions may extend beyond the exposed area. Drugs involved are sulfonamides, sulfonylureas, griseofulvin, chloroquine, chlorpromazine, carbamazepine. Drug dependence Drugs capable of altering mood and feelings are liable to repetitive use to derive euphoria, recreation, withdrawal from reality, social adjustment, etc. Drug dependence is a state in which use of drugs for personal satisfaction is accorded a higher priority than other basic needs, often in the face of known risks to health. Psychological dependence It is said to have developed when the individual believes that optimal state of wellbeing is achieved only through the actions of the drug. It may start as liking for the drug effects and may progress to compulsive drug use in some individuals who then lose control over the use of the drug. Obviously, certain degree of psychological dependence accompanies all patterns of self medication. Reinforcement is the ability of the drug to produce effects that the user enjoys and which make him/her wish to take it again or to induce drug seeking behaviour. Certain drugs (opioids, cocaine) are strong reinforcers, while others (benzodiazepines) are weak reinforcers.
Factors Causing Collapsing Tendency of Lungs Two factors are responsible for the collapsing tendency of lungs: 1 hiv infection horror stories generic 8 mg atacand free shipping. Elastic property of lung tissues: Elastic tissues of lungs show constant recoiling tendency and try to collapse the lungs 2 anti viral hand gel uk purchase atacand in india. Surface tension: It is the tension exerted by the fluid secreted from alveolar epithelium on the surface of alveolar membrane hiv infection onset purchase atacand 8mg with amex. Factors Preventing Collapsing Tendency of Lungs In spite of elastic property of lungs and surface tension in the alveoli of lungs antiviral vaccines atacand 8 mg discount, the collapsing tendency of lungs is prevented by two factors: 1. Intrapleural pressure: It is the pressure in the pleural cavity, which is always negative (see below). Because of negativity, it keeps the lungs expanded and prevents the collapsing tendency of lungs produced by the elastic tissues. It reduces surface tension and prevents the collapsing tendency produced by surface tension. Surfactant Surfactant is a surface acting material or agent that is responsible for lowering the surface tension of a fluid. Surfactant that lines the epithelium of the alveoli in lungs is known as pulmonary surfactant and it decreases the surface tension on the alveolar membrane. Source of secretion of pulmonary surfactant Pulmonary surfactant is secreted by two types of cells: 1. Characteristic feature of these cells is the presence of microvilli on their alveolar surface. Chemistry of surfactant Surfactant is a lipoprotein complex formed by lipids especially phospholipids, proteins and ions. Surfactant proteins are vital components of surfactant and the surfactant becomes inactive in the absence of proteins. These materials are synthesized in endoplasmic reticulum and stored in laminar bodies. By means of exocytosis, lipids and proteins of lamellar bodies are released into surface fluid lining the alveoli. Here, in the presence of surfactant proteins and calcium, the phospholipids are arranged into a lattice (meshwork) structure called tubular myelin. Tubular myelin is in turn converted into surfactant in the form of a film that spreads over the entire surface of alveoli. Factors necessary for the formation and spreading of surfactant Formation of surfactant requires many substances. Surfactant reduces the surface tension in the alveoli of lungs and prevents collapsing tendency of lungs. Chapter 120 t Mechanics of Respiration 685 Surfactant acts by the following mechanism: Phospholipid molecule in the surfactant has two portions. This surface of the phospholipid along with other portion spreads over the alveoli and reduces the surface tension. Surfactant is responsible for stabilization of the alveoli, which is necessary to withstand the collaps ing tendency. Soon after birth, the first breath starts because of the stimulation of respiratory centers by hypoxia and hypercapnea. Although the respiratory movements are attempted by the infant, the lungs tend to collapse repeatedly. And, the presence of surfactant in the alveoli prevents the lungs from collapsing. Another important function of surfactant is its role in defense within the lungs against infection and inflammation. Deficiency of surfactant occurs in adults also and it is called adult In addition, the deficiency of surfactant increases the susceptibility for bacterial and viral infections. Normal Values Respiratory pressures are always expressed in relation to atmospheric pressure, which is 760 mm Hg.
4mg atacand visa. The HIV/AIDS Epidemic: Where Does The World Stand?.